Parquet
- http://parquet.io/
- https://github.com/Parquet/parquet-format/blob/master/README.md
- https://github.com/Parquet/parquet-mr/wiki/The-striping-and-assembly-algorithms-from-the-Dremel-paper
- https://blog.twitter.com/2013/dremel-made-simple-with-parquet
- https://github.com/Parquet/parquet-format/blob/master/Encodings.md
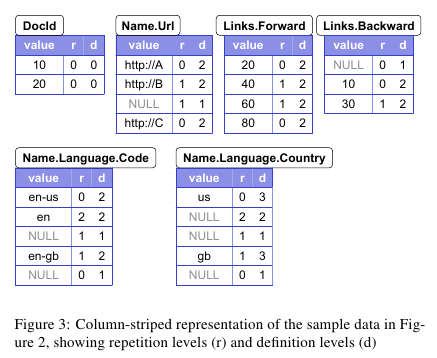
相比RCFile 和 ORCFile 而言,Parquet支持嵌套数据结构的schema. 至于Parquet如何从嵌套数据结构从抽取schema以及列存储格式,Parquer参考了Dremel 论文
在Dremel 论文里面讲到了使用两个辅助字段来支持列式存储嵌套数据结构。一个是repetition level, 一个是definition level. 这两个字段在这篇文章有更详细的解释。https://blog.twitter.com/2013/dremel-made-simple-with-parquet
- repetition level = n. 表示需要在[重复]层次级别为n的字段创建一个新结构并且存入value.
- definition level = n. 表示当前所在[可选或者是重复]层级上前n个字段是有定义的。这个字段是为了表示value = NULL设计的,如果 d < max(def-level)的话那么value必然为NULL.
https://github.com/Parquet/parquet-mr/wiki/The-striping-and-assembly-algorithms-from-the-Dremel-paper 给出了如何step by step地计算Dremel论文里面给出的例子,Dremel论文也在附录给出了具体算法

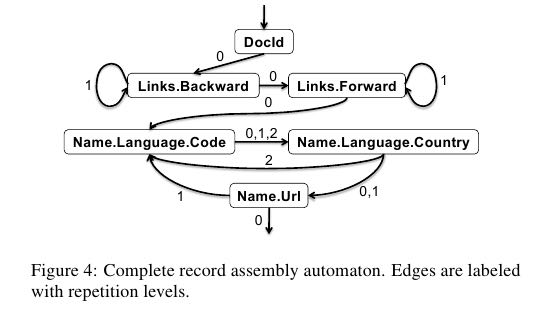
将columnar data组合成为记录这个过程成为record assembly. 具体算法在Dremel论文里面也有,基本原理是使用rep level来构建FSM,并且同时根据def level判断是否为NULL value. 并且可以只构建部分结构的状态机(如果我们不需要读取所有字段的话,那么这个特性就非常有用)
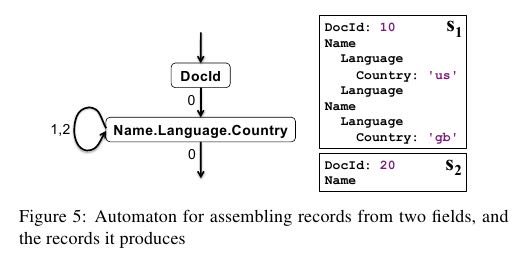
parquet实现有下面几个术语:
- Block (hdfs block): This means a block in hdfs and the meaning is unchanged for describing this file format. The file format is designed to work well on top of hdfs.
- File: A hdfs file that must include the metadata for the file. It does not need to actually contain the data.
- Row group: A logical horizontal partitioning of the data into rows. There is no physical structure that is guaranteed for a row group. A row group consists of a column chunk for each column in the dataset.
- Column chunk: A chunk of the data for a particular column. These live in a particular row group and is guaranteed to be contiguous in the file.(每个column chunk只存储一个row group下面的某一个column)
- Page: Column chunks are divided up into pages. A page is conceptually an indivisible unit (in terms of compression and encoding). There can be multiple page types which is interleaved in a column chunk.(在一个column chunk里面可能会有很多不同类型的page, 这些page作用也不尽相同。每个page是单独压缩和解压缩的,这样如果只需要访问部分record下面column的话就不用解压缩整个column chunk了)
Hierarchically, a file consists of one or more row groups. A row group contains exactly one column chunk per column. Column chunks contain one or more pages.
关于Row group size以及Page size配置
- Row group size: Larger row groups allow for larger column chunks which makes it possible to do larger sequential IO. Larger groups also require more buffering in the write path (or a two pass write). We recommend large row groups (512MB - 1GB). Since an entire row group might need to be read, we want it to completely fit on one HDFS block. Therefore, HDFS block sizes should also be set to be larger. An optimized read setup would be: 1GB row groups, 1GB HDFS block size, 1 HDFS block per HDFS file.
- Data page size: Data pages should be considered indivisible so smaller data pages allow for more fine grained reading (e.g. single row lookup). Larger page sizes incur less space overhead (less page headers) and potentially less parsing overhead (processing headers). Note: for sequential scans, it is not expected to read a page at a time; this is not the IO chunk. We recommend 8KB for page sizes.(这个参数是encoding和compression unit, 而不是IO unit)
大致文件格式如下,看上去和leveldb SSTable格式也非常类似。Chunk N表示第N个row group,
4-byte magic number "PAR1" <Column 1 Chunk 1 + Column Metadata> <Column 2 Chunk 1 + Column Metadata> ... <Column N Chunk 1 + Column Metadata> <Column 1 Chunk 2 + Column Metadata> <Column 2 Chunk 2 + Column Metadata> ... <Column N Chunk 2 + Column Metadata> ... <Column 1 Chunk M + Column Metadata> <Column 2 Chunk M + Column Metadata> ... <Column N Chunk M + Column Metadata> File Metadata 4-byte length in bytes of file metadata 4-byte magic number "PAR1"
下图表示如何使用这个文件。注意这里repetition level和definition level是单独存放的。因为它们都是相对较小的整数所以可以使用RLE或者是bit-pack来达到非常高的压缩比。
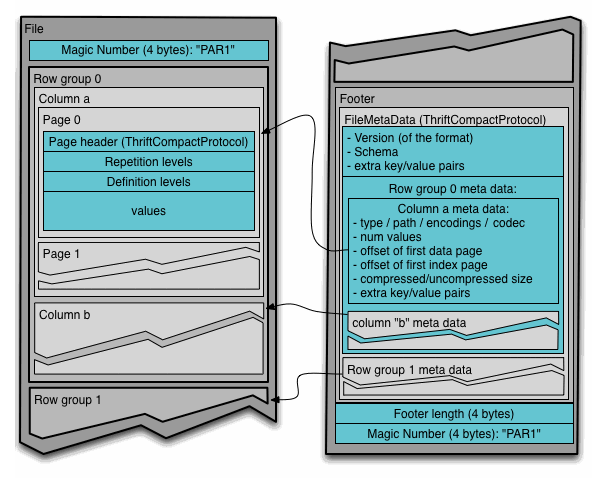
There are three types of metadata: file metadata, column (chunk) metadata and page header metadata. All thrift structures are serialized using the TCompactProtocol.
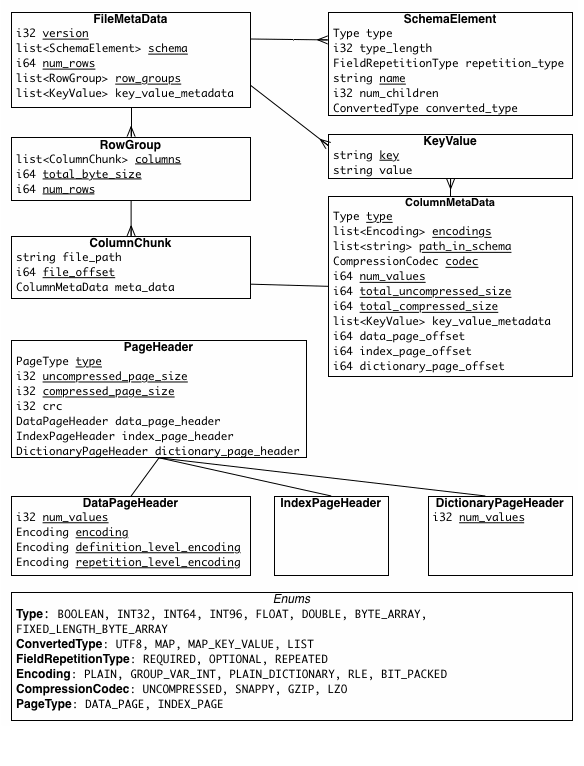
我觉得在DataPageHeader里面还应该存放num_rows(num_values),表示这个page里面到底有多少个record. 这样我们才能够提过一些page读取到某个record. 或许这个信息已经存放在IndexPageHeader里面了?这里DictionaryPageHeader是为后面提到的Encoding使用的。
Parquet针对homogeneous columnar data提供了很多种压缩算法 https://github.com/Parquet/parquet-format/blob/master/Encodings.md
- Plain: (PLAIN = 0) 针对所有类型数据
- Dictionary Encoding (PLAIN_DICTIONARY = 2) 针对非byte_array数据包括整数和浮点数
- Run Length Encoding / Bit-Packing Hybrid (RLE = 3) 针对整数
- Bit-packed (Deprecated) (BIT_PACKED = 4) 针对整数
- Delta Encoding (DELTA_BINARY_PACKED = 5) 针对整数
- Delta-length byte array: (DELTA_LENGTH_BYTE_ARRAY = 6) 针对byte_array
- Delta Strings: (DELTA_BYTE_ARRAY = 7) 针对byte_array
Dictionary Encoding (PLAIN_DICTIONARY = 2)
The dictionary encoding builds a dictionary of values encountered in a given column. The dictionary will be stored in a dictionary page per column chunk. The values are stored as integers using the RLE/Bit-Packing Hybrid encoding described above. If the dictionary grows too big, whether in size or number of distinct values, the encoding will fall back to the plain encoding. The dictionary page is written first, before the data pages of the column chunk.
Dictionary page format: the entries in the dictionary - in dictionary order - using the plain encoding described above. Data page format: the bit width used to encode the entry ids stored as 1 byte (max bit width = 32), followed by the values encoded using RLE/Bit packed described above (with the given bit width).
Run Length Encoding / Bit-Packing Hybrid (RLE = 3) & Bit-packed (Deprecated) (BIT_PACKED = 4)
首先说4这个压缩方法,实际上就是将所有values的bit表示连接在一起,存放顺序是从MSB到LSB.
For example, the numbers 1 through 7 using bit width 3:
dec value: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 bit value: 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 bit label: ABC DEF GHI JKL MNO PQR STU VWX bit value: 00000101 00111001 01110111 bit label: ABCDEFGH IJKLMNOP QRSTUVWX
对于3里面bit-packing压缩方法一样,但是存放顺序是从LSB到MSB,还是以上面为例
bit value: 10001000 11000110 11111010 bit label: HIDEFABC RMNOJKLG VWXSTUPQ
压缩方法3里面不仅仅支持bit-packing, 还支持RLE。所谓RLE就是寻找重复数字,比如00000就可以表示成为<5><0>.
为了混合RLE和bit-packing, 压缩方法3在存储上使用单独标志位标记使用哪种方法
rle-bit-packed-hybrid: <length> <encoded-data> length := length of the <encoded-data> in bytes stored as 4 bytes little endian encoded-data := <run>* run := <bit-packed-run> | <rle-run> bit-packed-run := <bit-packed-header> <bit-packed-values> bit-packed-header := varint-encode(<bit-pack-count> << 1 | 1) // we always bit-pack a multiple of 8 values at a time, so we only store the number of values / 8 bit-pack-count := (number of values in this run) / 8 bit-packed-values := *see 1 below* rle-run := <rle-header> <repeated-value> rle-header := varint-encode( (number of times repeated) << 1) repeated-value := value that is repeated, using a fixed-width of round-up-to-next-byte(bit-width)
varint-encode() is ULEB-128 encoding, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Variable-length_quantity
Delta Encoding (DELTA_BINARY_PACKED = 5)
This encoding is adapted from the Binary packing described in "Decoding billions of integers per second through vectorization" by D. Lemire and L. Boytsov. 这个方法应该非常适合向量指令。
Delta encoding consists of a header followed by blocks of delta encoded values binary packed. Each block is made of miniblocks, each of them binary packed with its own bit width. When there are not enough values to encode a full block we pad with zeros (added to the frame of reference). The header is defined as follows:
<block size in values> <number of miniblocks in a block> <total value count> <first value>
- the block size is a multiple of 128 stored as VLQ int(values个数必须整除128)
- the miniblock count per block is a diviser of the block size stored as VLQ int
- the number of values in the miniblock is a multiple of 32.(每个minblocks里面value个数整除32)
- the total value count is stored as a VLQ int
- the first value is stored as a zigzag VLQ int
Each block contains
<min delta> <list of bitwidths of miniblocks> <miniblocks>
- the min delta is a VLQ int (we compute a minimum as we need positive integers for bit packing) (将所有的delta转换成为正数)
- the bitwidth of each block is stored as a byte(每个minblocks使用的bitwidth)
- each miniblock is a list of bit packed ints according to the bit width stored at the begining of the block(minblocks里面使用bit-packed压缩)
每个minblocks应该都可以被向量指令处理,min-delta引入是为了处理正数加快速度。而为每个minblocks引入不同的bitwidth可以有效减少存储空间。
Delta-length byte array: (DELTA_LENGTH_BYTE_ARRAY = 6)
将byte_size和byte_data分开,然后将byte_size聚合存放并且使用压缩方法5. For example, if the data was "Hello", "World", "Foobar", "ABCDEF": The encoded data would be DeltaEncoding(5, 5, 6, 6) "HelloWorldFoobarABCDEF"
Delta Strings: (DELTA_BYTE_ARRAY = 7)
This is also known as incremental encoding or front compression: for each element in a sequence of strings, store the prefix length of the previous entry plus the suffix. For a longer description, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Incremental_encoding. This is stored as a sequence of delta-encoded prefix lengths (DELTA_BINARY_PACKED), followed by the suffixes encoded as delta length byte arrays (DELTA_LENGTH_BYTE_ARRAY).
举个例子"AB", "ABC", "ABCD", 前缀压缩之后成为<0>"AB", <2>"C", <3>"D". 最终压缩结果是DeltaEncoding(0,2,3) DeltaEncoding(2,1,1) "ABCD".