HBase
Table of Contents
- 1. 单节点搭建
- 2. table configuration
- 3. hbase shell
- 4. hbase hbck
- 5. hbase increment
- 6. python client
- 7. 获取集群运行状况
- 8. bulk load
- 9. hbase merge
- 10. hbase export/import
- 11. region can't be assigned
- 12. output error
- 13. zookeeper session expired
- 14. lease expired exception
- 15. filesystem not available
- 16. error block recovery
- 17. dyq's hbase representation
- 18. put大小限制分析
- 19. put过程代码分析
- 20. asynchbase
- 21. clock skew
- 22. hbase join
1. 单节点搭建
修改conf/hbase-site.xml,增加选项
<property> <property> <name>hbase.cluster.distributed</name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <name>hbase.zookeeper.quorum</name> <value>localhost</value> </property> <name>hbase.rootdir</name> <value>hdfs://localhost:8020/user/dirlt/hbase</value> </property>
2. table configuration
- DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING => 'FAST_DIFF'(PREFIX,DIFF) # block压缩算法(偏向应用层)
- ENCODE_ON_DISK => 'false' # 以上encoding是否需要作用在disk上
- BLOOMFILTER => 'ROW'(ROWCOL) # 按照row还是按照row+qualifier做bloom filter.
- COMPRESSION => 'SNAPPY' # block压缩算法(偏向系统层)
- BLOCKSIZE => '32768' # 对于随机查询高的table,blocksize缩小可以减少LRUCache使用
- VERSIONS => '100' # 保存历史版本数目
- NAME => 'info' # column family
3. hbase shell
- scan 'test'
- STARTROW=>'xyz'
- ENDROW=>'uvw'
- COLUMN=>['cf:url']
- LIMIT=>10
- VERSIONS=>3
- count 'test'
- create 'test', { NAME=>'cf' }
- get 'test', 'rowkey',
- COLUMN = > ['cf:url']
- put 'test', 'rowkey', 'cf:url', 'value'
- balance_switch (true/false) # 是否允许balance
- balancer # 执行balance. 和balance_switch有关
- 如果存在region in transition的话,那么直接返回false
- assign <region_name>
- 如果存在某些region in transition一直没有成功的话,说明这个region一直处于unassigned状态,可以手动assign.
- hadoop - Repair HBase table (unassigned region in transition) - Stack Overflow : http://stackoverflow.com/questions/11010167/repair-hbase-table-unassigned-region-in-transition
- flush 'test' 将in-memory数据刷到文件中
- compact / major_compact 'test' 将表格做major compaction.
如果需要输入二进制的话,可以使用\x1e这样的方式表示,但是务必使用". 比如"stat:abc\x1exyz"
4. hbase hbck
- 默认检查hbase状态
- 如果出现不一致状态,可以使用参数 -fix 来修复 #note: 存在丢失数据的风险
5. hbase increment
6. python client
使用python来访问hbase确实可以很大地提高开发效率,但是通过thrift server来进行中转的话对于性能还是存在影响的,因此比较适合测试。
- 启动thrift server
- hbase-deamon.sh start thrift
- 安装happybase
- pip install happybase
- github: https://github.com/wbolster/happybase
- doc: http://happybase.readthedocs.org/en/latest/index.html
使用起来还是比较简单的,documentation也非常详细。
#note: 发现还是存在一些不兼容的thrift协议,比如使用scan似乎就存在问题
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "./hbase.py", line 20, in <module>
for k,v in iters:
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/happybase/api.py", line 567, in scan
scan_id = client.scannerOpenWithScan(self.name, scan)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/happybase/hbase/Hbase.py", line 1716, in scannerOpenWithScan
return self.recv_scannerOpenWithScan()
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/happybase/hbase/Hbase.py", line 1733, in recv_scannerOpenWithScan
raise x
thrift.Thrift.TApplicationException: Invalid method name: 'scannerOpenWithScan'
7. 获取集群运行状况
- code on github
- HBaseAdmin可以获取节点信息
- HTable可以获取table信息
8. bulk load
- http://hbase.apache.org/book/arch.bulk.load.html
- Preparing data via a MapReduce job
- 将输入文件转换成为HFile格式
- code on github
- region,reduce,output对应,也就是说有多少个region就有多少个reduce
- #note: 所以需要关注region分布。如果过于集中的话需要考虑使用做pre-split或者是将key做hash-prefix等
- configureIncrementalLoad会改写reducer实现,所以这个转换过程只能够由单独任务完成。
- In order to function efficiently, HFileOutputFormat must be configured such that each output HFile fits within a single region. In order to do this, jobs whose output will be bulk loaded into HBase use Hadoop's TotalOrderPartitioner class to partition the map output into disjoint ranges of the key space, corresponding to the key ranges of the regions in the table. HFileOutputFormat includes a convenience function, configureIncrementalLoad(), which automatically sets up a TotalOrderPartitioner based on the current region boundaries of a table.
- Completing the data load
- 将上步产生的HFile移动到相应目录并且通知对应的rs
- If the region boundaries have changed during the course of bulk load preparation, or between the preparation and completion steps, the completebulkloads utility will automatically split the data files into pieces corresponding to the new boundaries. This process is not optimally efficient, so users should take care to minimize the delay between preparing a bulk load and importing it into the cluster, especially if other clients are simultaneously loading data through other means.
- 如果在产生HFile和load之间rs出现分裂的话,bulkload工具能够自动处理,但是相对来说效率不是最佳。
- hadoop jar hbase-VERSION.jar completebulkload [-c /path/to/hbase/config/hbase-site.xml] /user/todd/myoutput mytable
- #note: 实际上上面命令可能会出现权限问题,如果转换程序输出是hdfs owner的话,而要将文件移动到hbase那么必须是hbase owner. 所以通常使用下面命令完成
- sudo -u hdfs hadoop fs -chmod -R 0777 <hfile-path> # 修改权限
- sudo -u hdfs hadoop fs -chown -R hbase <hfile-path> # 修改owner
- sudo -u hbase hadoop jar /usr/lib/hbase/hbase-0.94.6-cdh4.3.0-security.jar completebulkload <hfile-path> <table>
9. hbase merge
- #note: 需要停表或者是停集群
- hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Merge <table> <region1> <region2>
- 工作原理大致是
- 读取region1,region2对应hbase的目录下面数据文件
- 检查.regioninfo是否相连
- 合并文件内容输出到另外一个目录下面
- 修改hbase的.META文件信息
- #note: 这个对于修复数据非常有效
10. hbase export/import
使用导出导入功能可以用来做数据迁移,这只是数据迁移的一种办法。这里介绍了许多办法 http://hbase.apache.org/book/ops.backup.html 包括
- distcp
- replication
- copy table
- export / import
运行原理我猜测是export对table做scan操作然后转换成为Put/Del对象,然后import就是执行这些对象。 因为export这里允许执行时间戳,所以实际上可以完成增量备份
Export
Usage: Export [-D <property=value>]* <tablename> <outputdir> [<versions> [<starttime> [<endtime>]] [^[regex pattern] or [Prefix] to filter]]
Note: -D properties will be applied to the conf used. For example: -D mapred.output.compress=true -D mapred.output.compression.codec=org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec -D mapred.output.compression.type=BLOCK Additionally, the following SCAN properties can be specified to control/limit what is exported.. -D hbase.mapreduce.scan.column.family=<familyName> -D hbase.mapreduce.include.deleted.rows=true For performance consider the following properties: -Dhbase.client.scanner.caching=100 -Dmapred.map.tasks.speculative.execution=false -Dmapred.reduce.tasks.speculative.execution=false For tables with very wide rows consider setting the batch size as below: -Dhbase.export.scanner.batch=10
Import
Usage: Import [options] <tablename> <inputdir> By default Import will load data directly into HBase. To instead generate HFiles of data to prepare for a bulk data load, pass the option: -Dimport.bulk.output=/path/for/output To apply a generic org.apache.hadoop.hbase.filter.Filter to the input, use -Dimport.filter.class=<name of filter class> -Dimport.filter.args=<comma separated list of args for filter NOTE: The filter will be applied BEFORE doing key renames via the HBASE_IMPORTER_RENAME_CFS property. Futher, filters will only use theFilter#filterKeyValue(KeyValue) method to determine if the KeyValue should be added; Filter.ReturnCode#INCLUDE and #INCLUDE_AND_NEXT_COL will be considered as including the KeyValue. For performance consider the following options: -Dmapred.map.tasks.speculative.execution=false -Dmapred.reduce.tasks.speculative.execution=false
按照链接里面的命令执行,bin/hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.Export可能会出现下面的问题
13/12/17 16:38:47 ERROR security.UserGroupInformation: PriviledgedActionException as:dirlt (auth:SIMPLE) cause:java.io.IOException: Cannot initialize Cluster. Please check your configuration for mapreduce.framework.name and the correspond server addresses.
Exception in thread "main" java.io.IOException: Cannot initialize Cluster. Please check your configuration for mapreduce.framework.name and the correspond server addresses.
at org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Cluster.initialize(Cluster.java:121)
at org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Cluster.<init>(Cluster.java:83)
at org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Cluster.<init>(Cluster.java:76)
at org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job$10.run(Job.java:1239)
at org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job$10.run(Job.java:1235)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at javax.security.auth.Subject.doAs(Subject.java:416)
at org.apache.hadoop.security.UserGroupInformation.doAs(UserGroupInformation.java:1408)
at org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job.connect(Job.java:1234)
at org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job.submit(Job.java:1263)
at org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job.waitForCompletion(Job.java:1287)
at org.apache.hadoop.examples.QuasiMonteCarlo.estimatePi(QuasiMonteCarlo.java:306)
at org.apache.hadoop.examples.QuasiMonteCarlo.run(QuasiMonteCarlo.java:351)
at org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner.run(ToolRunner.java:70)
at org.apache.hadoop.examples.QuasiMonteCarlo.main(QuasiMonteCarlo.java:360)
我这里的原因是因为hbase使用的是mapreduce2的接口(通过上面stacktrace里面行信息,发现Job类对应的是mapreduce2里面的实现),而我运行的是mapreduce1的集群,所以导致没有办法提交作业。
解决办法是使用hadoop来执行,而不要使用hbase来执行
hadoop jar ~/utils/hbase-0.94.6-cdh4.3.0/hbase-0.94.6-cdh4.3.0-security.jar export/import
11. region can't be assigned
region一直assign不上,观察曾经尝试被assigned的节点出现下面的错误
java.io.IOException: java.io.IOException: java.io.FileNotFoundException: File does not exist: /hbase/installhistory/2f1b909bb15ce5960d72a1773902085c/install/240086423354424bb32d647fab6f9b98
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.INodeFile.valueOf(INodeFile.java:39)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem.getBlockLocationsUpdateTimes(FSNamesystem.java:1341)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem.getBlockLocationsInt(FSNamesystem.java:1293)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem.getBlockLocations(FSNamesystem.java:1269)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem.getBlockLocations(FSNamesystem.java:1242)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.NameNodeRpcServer.getBlockLocations(NameNodeRpcServer.java:392)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocolPB.ClientNamenodeProtocolServerSideTranslatorPB.getBlockLocations(ClientNamenodeProtocolServerSideTranslatorPB.java:172)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocol.proto.ClientNamenodeProtocolProtos$ClientNamenodeProtocol$2.callBlockingMethod(ClientNamenodeProtocolProtos.java:44938)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.ProtobufRpcEngine$Server$ProtoBufRpcInvoker.call(ProtobufRpcEngine.java:453)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RPC$Server.call(RPC.java:1002)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server$Handler$1.run(Server.java:1701)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server$Handler$1.run(Server.java:1697)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at javax.security.auth.Subject.doAs(Subject.java:396)
at org.apache.hadoop.security.UserGroupInformation.doAs(UserGroupInformation.java:1408)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server$Handler.run(Server.java:1695)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegion.initializeRegionInternals(HRegion.java:607)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegion.initialize(HRegion.java:520)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegion.openHRegion(HRegion.java:4313)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegion.openHRegion(HRegion.java:4261)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.handler.OpenRegionHandler.openRegion(OpenRegionHandler.java:329)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.handler.OpenRegionHandler.process(OpenRegionHandler.java:100)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.executor.EventHandler.run(EventHandler.java:175)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.runTask(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:895)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:918)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:662)
我们曾经遇到这个问题是因为集群数据出现不一致的情况。观察WebUI上实际上它查找另外一个encodedName 6ef7e4f2c72929d789f63baba2f13d4e. 这个路径在HDFS中存在并且文件名称和240086423354424bb32d647fab6f9b98完全一致。
当时我们处理的办法是将6ef7e4f2c72929d789f63baba2f13d4e重命名为2f1b909bb15ce5960d72a1773902085c。实际上这是一个错误的做法,因为2f1b909bb15ce5960d72a1773902085c这个regionName在META里面根本不存在。出现这样的情况是因为当时在6ef7e4f2c72929d789f63baba2f13d4e下面存在一个文件 240086423354424bb32d647fab6f9b98.2f1b909bb15ce5960d72a1773902085c 。这个文件大小非常小,我们当时怀疑是一个类似软链接的文件,当读取240086423354424bb32d647fab6f9b98这个文件的时候,如果存在link文件的话,那么就会转移到另外一个directory下面读取。 所以我们直接将这个link文件删除了,结果region瞬间加载成功
#note: 如果需要强制停止assign一个节点的话,只能进入zookeeper的/hbase/unassigned目录将下面节点完全删除,hbase shell的unassign命令只是针对那些assign成功的region有效
12. output error
2013.04.07 AttachAppkeyToDeviceInfo失败很多次,都是因为连接hbase很多次失败。观察发现每次task都是连接某一个regionserver失败。日志中出现很多下面这样的错误:
2013-04-12 06:02:25,978 WARN org.apache.hadoop.ipc.HBaseServer: IPC Server Responder, call multi(org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.MultiAction@9c31dfd) from 10.11.0.13:25641: output error
2013-04-12 06:02:25,987 WARN org.apache.hadoop.ipc.HBaseServer: IPC Server handler 18 on 60020 caught: java.nio.channels.ClosedChannelException
at sun.nio.ch.SocketChannelImpl.ensureWriteOpen(SocketChannelImpl.java:133)
at sun.nio.ch.SocketChannelImpl.write(SocketChannelImpl.java:324)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HBaseServer.channelIO(HBaseServer.java:1389)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HBaseServer.channelWrite(HBaseServer.java:1341)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HBaseServer$Responder.processResponse(HBaseServer.java:727)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HBaseServer$Responder.doRespond(HBaseServer.java:792)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HBaseServer$Handler.run(HBaseServer.java:1083)
主要原因是client操作超时链接关闭所以有closed channel exception这样的异常。当时这个regionserver在做compaction,造成压力巨大。之后叶总做了balance之后恢复正常。因为这个情况离现在比较久了,所以没有办法很细粒度地从ganglia里面抽取当时集群数据。
这个情况下面需要分析压力巨大的原因。 就我们现在情况来说比较可能是分配region多或者是数据分布不均匀。
除了multi action之外,还有get,next等hbase operation都可能会得到
13. zookeeper session expired
HBase中出现如下FATAL信息。单独看这个日志只是知道zookeeper长时间没有汇报断开连接,但是具体是什么原因需要分析上下文
2013-04-12 08:20:36,063 FATAL org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer: ABORTING region server serverName=dp18.umeng.com,60020,1364871259512, load=(requests=14830, regions=211, used
Heap=12618, maxHeap=13973): regionserver:60020-0x53c04ec6699f092 regionserver:60020-0x53c04ec6699f092 received expired from ZooKeeper, aborting
org.apache.zookeeper.KeeperException$SessionExpiredException: KeeperErrorCode = Session expired
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.zookeeper.ZooKeeperWatcher.connectionEvent(ZooKeeperWatcher.java:353)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.zookeeper.ZooKeeperWatcher.process(ZooKeeperWatcher.java:271)
at org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn$EventThread.processEvent(ClientCnxn.java:531)
at org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn$EventThread.run(ClientCnxn.java:507)
常见的上下文如下。实际上这些INFO日志都有说明即将和zookeeper断开。 主要是因为GC时间过长而不是网络partition(现在是在同机房)
2013-04-12 08:20:35,545 INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Client session timed out, have not heard from server in 43293ms for sessionid 0x53c04ec6699f092, closing socket connection and at tempting reconnect 2013-04-12 08:20:35,545 INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Client session timed out, have not heard from server in 45375ms for sessionid 0x53c04ec6699f093, closing socket connection and at tempting reconnect 2013-04-12 08:20:36,028 INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Opening socket connection to server dp30/10.11.0.30:2181 2013-04-12 08:20:36,028 INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Socket connection established to dp30/10.11.0.30:2181, initiating session 2013-04-12 08:20:36,035 INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Unable to reconnect to ZooKeeper service, session 0x53c04ec6699f093 has expired, closing socket connection 2013-04-12 08:20:36,043 INFO org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HConnectionManager$HConnectionImplementation: This client just lost it's session with ZooKeeper, trying to reconnect. 2013-04-12 08:20:36,044 INFO org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HConnectionManager$HConnectionImplementation: Trying to reconnect to zookeeper 2013-04-12 08:20:36,046 INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ZooKeeper: Initiating client connection, connectString=dp30:2181,dp20:2181,dp10:2181,dp5:2181,dp40:2181 sessionTimeout=180000 watcher=hconnec tion 2013-04-12 08:20:36,047 INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Opening socket connection to server dp20/10.11.0.20:2181 2013-04-12 08:20:36,050 INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Socket connection established to dp20/10.11.0.20:2181, initiating session 2013-04-12 08:20:36,058 INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Opening socket connection to server dp5/10.11.0.5:2181 2013-04-12 08:20:36,059 INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Socket connection established to dp5/10.11.0.5:2181, initiating session 2013-04-12 08:20:36,063 INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Unable to reconnect to ZooKeeper service, session 0x53c04ec6699f092 has expired, closing socket connection 2013-04-12 08:20:36,071 INFO org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HConnectionManager$HConnectionImplementation: Reconnected successfully. This disconnect could have been caused by a network partition or a long-running GC pause, either way it's recommended that you verify your environment.(GC时间太长造成zookeeper session expired)
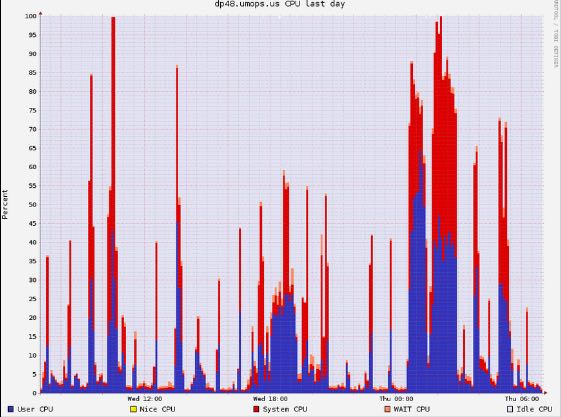
CPU开销比较大也是可能原因 , @2013-05-16 01:53:46 dp48 也出现过这样的情况但是上下文里面没有显示是GC造成的开销,毕竟可以看到memory使用比较小
2013-05-16 01:53:46,449 FATAL org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer: ABORTING region server serverName=dp48.umops.us,60020,1368628743704, load=(requests=0, regions=5, usedHeap=108, maxHeap=13952): regionserver:60020-0x43e6d9fa1317bba-0x43e6d9fa1317bba regionserver:60020-0x43e6d9fa1317bba-0x43e6d9fa1317bba received expired from ZooKeeper, aborting
org.apache.zookeeper.KeeperException$SessionExpiredException: KeeperErrorCode = Session expired
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.zookeeper.ZooKeeperWatcher.connectionEvent(ZooKeeperWatcher.java:353)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.zookeeper.ZooKeeperWatcher.process(ZooKeeperWatcher.java:271)
at org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn$EventThread.processEvent(ClientCnxn.java:531)
at org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn$EventThread.run(ClientCnxn.java:507)
下面是从ganglia里面来的当时的负载情况
14. lease expired exception
2013-04-11 08:07:34,121 ERROR org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer: Close and delete failed
org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.LeaseExpiredException: org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.LeaseExpiredException: No lease on /hbase/.logs/dp22.umeng.com,60020,1365284229083/dp22.umeng.com%3A60020.1365638781277 File does
not exist. [Lease. Holder: DFSClient_hb_rs_dp22.umeng.com,60020,1365284229083_1365284230001, pendingcreates: 2]
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem.checkLease(FSNamesystem.java:1593)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem.checkLease(FSNamesystem.java:1584)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem.completeFileInternal(FSNamesystem.java:1639)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem.completeFile(FSNamesystem.java:1627)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.NameNode.complete(NameNode.java:687)
at sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor25.invoke(Unknown Source)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RPC$Server.call(RPC.java:557)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server$Handler$1.run(Server.java:1434)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server$Handler$1.run(Server.java:1430)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at javax.security.auth.Subject.doAs(Subject.java:396)
at org.apache.hadoop.security.UserGroupInformation.doAs(UserGroupInformation.java:1157)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server$Handler.run(Server.java:1428)
at sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.java:39)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.java:27)
at java.lang.reflect.Constructor.newInstance(Constructor.java:513)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.RemoteExceptionHandler.decodeRemoteException(RemoteExceptionHandler.java:96)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.RemoteExceptionHandler.checkThrowable(RemoteExceptionHandler.java:48)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer.closeWAL(HRegionServer.java:795)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer.run(HRegionServer.java:664)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:619)
这个log通常出现在regionserver挂掉之前。通常regionserver因为某种原因从zookeeper上掉线,需要flush以及删除region对应的WAL,而如果接管的regionserver在此之前已经读取完成WAL并且删除的话,那么就会出现如上文件已经不存在的错误。
15. filesystem not available
hbase出现如下fatal日志,并且可以看到这个日志造成region server退出。
#note: 个人觉得原因是namenode和datanode不能够支撑这些请求压力,可以适当调大处理线程数目。这种情况下面也会出现很多Failed to connect to datanode的情况
2013-05-13 04:10:11,256 FATAL org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer: ABORTING region server serverName=dp31.umeng.com,60020,1367978709152, load=(requests=55849, regions=158, usedHeap=6520, maxHeap=13962): File System not available
java.io.IOException: File system is not available
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.FSUtils.checkFileSystemAvailable(FSUtils.java:135)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer.checkFileSystem(HRegionServer.java:1034)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer.cleanup(HRegionServer.java:980)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer.cleanup(HRegionServer.java:955)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer.get(HRegionServer.java:1695)
at sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor11.invoke(Unknown Source)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HBaseRPC$Server.call(HBaseRPC.java:570)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HBaseServer$Handler.run(HBaseServer.java:1039)
Caused by: java.io.IOException: java.lang.InterruptedException
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Client.call(Client.java:1086)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RPC$Invoker.invoke(RPC.java:226)
at $Proxy5.getFileInfo(Unknown Source)
at sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor5.invoke(Unknown Source)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at org.apache.hadoop.io.retry.RetryInvocationHandler.invokeMethod(RetryInvocationHandler.java:82)
at org.apache.hadoop.io.retry.RetryInvocationHandler.invoke(RetryInvocationHandler.java:59)
at $Proxy5.getFileInfo(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DFSClient.getFileInfo(DFSClient.java:832)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DistributedFileSystem.getFileStatus(DistributedFileSystem.java:558)
at org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem.exists(FileSystem.java:797)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.FSUtils.checkFileSystemAvailable(FSUtils.java:124)
... 9 more
Caused by: java.lang.InterruptedException
at java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.acquireSharedInterruptibly(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java:1279)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask$Sync.innerGet(FutureTask.java:218)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.get(FutureTask.java:83)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Client$Connection.sendParam(Client.java:790)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Client.call(Client.java:1080)
2013-05-13 04:11:11,428 INFO org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer: STOPPED: File System not available
问题是hbase如何判断filesystem是否available的呢?从代码里面看是这样的, 这个过程只是直接和namenode进行交互。
public static void checkFileSystemAvailable(final FileSystem fs)
throws IOException {
if (!(fs instanceof DistributedFileSystem)) {
return;
}
IOException exception = null;
DistributedFileSystem dfs = (DistributedFileSystem) fs;
try {
if (dfs.exists(new Path("/"))) {
return;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
exception = RemoteExceptionHandler.checkIOException(e);
}
try {
fs.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error("file system close failed: ", e);
}
IOException io = new IOException("File system is not available");
io.initCause(exception);
throw io;
}
16. error block recovery
在dp47上面出现如下日志:
GS这里表示generation stamp, 对应的是creation time of file. 从日志里面分析应该是hdfs文件已经被修改过了,所以原来的datanode对应的block已经不存在了。
2013-05-13 01:16:31,881 WARN org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DFSClient: Error Recovery for block blk_-8113206033894163645_85507011 failed because recovery from primary datanode 10.11.0.47:50010 failed 4 times. Pipeline was 10.11.0.47:50010. Will retry...
2013-05-13 01:16:32,900 WARN org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DFSClient: Failed recovery attempt #4 from primary datanode 10.11.0.47:50010
org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RemoteException: org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RemoteException: java.io.IOException: blk_-8113206033894163645_85507011 has out of date GS 85507011 found 85507383, may already be committed
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.FSNamesystem.nextGenerationStampForBlock(FSNamesystem.java:5383)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.NameNode.nextGenerationStamp(NameNode.java:717)
at sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor29.invoke(Unknown Source)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RPC$Server.call(RPC.java:557)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server$Handler$1.run(Server.java:1434)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server$Handler$1.run(Server.java:1430)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at javax.security.auth.Subject.doAs(Subject.java:396)
at org.apache.hadoop.security.UserGroupInformation.doAs(UserGroupInformation.java:1157)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server$Handler.run(Server.java:1428)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Client.call(Client.java:1107)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RPC$Invoker.invoke(RPC.java:226)
at $Proxy4.nextGenerationStamp(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.datanode.DataNode.syncBlock(DataNode.java:2049)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.datanode.DataNode.recoverBlock(DataNode.java:2017)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.datanode.DataNode.recoverBlock(DataNode.java:2097)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:39)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RPC$Server.call(RPC.java:557)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server$Handler$1.run(Server.java:1434)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server$Handler$1.run(Server.java:1430)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at javax.security.auth.Subject.doAs(Subject.java:396)
at org.apache.hadoop.security.UserGroupInformation.doAs(UserGroupInformation.java:1157)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Server$Handler.run(Server.java:1428)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Client.call(Client.java:1107)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RPC$Invoker.invoke(RPC.java:226)
at $Proxy10.recoverBlock(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DFSClient$DFSOutputStream.processDatanodeError(DFSClient.java:3118)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DFSClient$DFSOutputStream.access$1900(DFSClient.java:2627)
at org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DFSClient$DFSOutputStream$DataStreamer.run(DFSClient.java:2799)
17. dyq's hbase representation
@ 2012-08-16
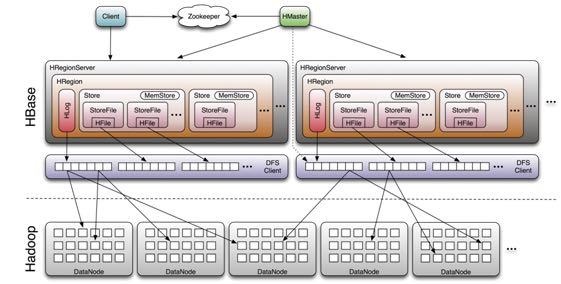
HRegion类似于tablet,每个HRegion有很多Store存储不同的column family。
对于memstore内存大小限制的话,有两个方面:
- HRegion如果总体内存比较大的话,那么会选择几个Store里面的memstore进行flush
- 如果Store里面的memstore本身比较大的话,也会进行flush
scan过程大致是这样的:
- 首先scanner得到memstore以及所有的hfile,以及这个似乎时候的timestamp(hbase使用timestamp作为version)进行归并排序。
- 如果期间memstore发生写,或者是flush,或者是进行compaction的话,那么会通知scanner
- scanner会重新组织这些内容,根据上次读取到的value,忽路duplicated的数据。
这样的好处就是通常在scanner的时候不会阻塞其他操作。
但是我看了一下leveldb代码,觉得实现上更好。对于immutable memtable以及memtable做引用计数,在iterator里面保存两个table。 如果memtable compaction之后的话,那么直接创建一个新的memtable即可。原有的table在iterator销毁的时候就会自动释放。
对于column family是可以设置超时时间的。在进行flush或者是compaction的时候,会判断这个value是否超过ttl。如果超过ttl的话那么就会直接丢弃。
18. put大小限制分析
在HTable.validatePut对put大小进行了限制
// validate for well-formedness
private void validatePut(final Put put) throws IllegalArgumentException{
if (put.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No columns to insert");
}
if (maxKeyValueSize > 0) {
for (List<KeyValue> list : put.getFamilyMap().values()) {
for (KeyValue kv : list) {
if (kv.getLength() > maxKeyValueSize) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("KeyValue size too large");
}
}
}
}
}
这里maxKeyValueSize是从配置文件里面读取出来的, this.maxKeyValueSize = conf.getInt("hbase.client.keyvalue.maxsize", -1); 因此可以修改hbase.client.keyvalue.maxsize来修改大小。 从实现上看这个大小应该是在client端进行限制的,个人推测在server端应该是没有大小限制的。
另外如果put是empty的话会抛出异常,因此在调用put之前最好判断put.isEmpty().
#note: 实际在server端也还是有大小限制的,可以看代码HBaseConfiguration.create
public static Configuration addHbaseResources(Configuration conf) {
conf.addResource("hbase-default.xml");
conf.addResource("hbase-site.xml");
checkDefaultsVersion(conf);
checkForClusterFreeMemoryLimit(conf);
return conf;
}
可以看到加载了hbase-default.xml这个文件。这个文件是在hbase package自带的,默认值为10485760 = 10M
19. put过程代码分析
最后都走到了下面这个方法,可以看到对于每次put并不是立即去写hbase的,除非有特殊开关autoFlush. writeBuffer是一个ArrayList用来hold住所有需要write的put.默认autoFlush=false,所以会缓存到writeBufferSize大小才会commit,而大小是通过heapSize来得到的。而writeBufferSize是通过hbase.client.write.buffer这个属性配置的,默认是2097152=2M
private void doPut(final List<Put> puts) throws IOException {
for (Put put : puts) {
validatePut(put);
writeBuffer.add(put);
currentWriteBufferSize += put.heapSize();
}
if (autoFlush || currentWriteBufferSize > writeBufferSize) {
flushCommits();
}
}
在flushCommits里面会在Connection上面去将这个writeBuffer写出去,如果失败的话那么会重新构造这个writeBuffer以及currentWriteBufferSize,注释里面也说了在这个操作里面会修改这些字段。 #note: 从下面的实现可以看到,writeBuffer里面剩余的都是没有成功的Put
public void flushCommits() throws IOException {
try {
connection.processBatchOfPuts(writeBuffer, tableName, pool);
} finally {
if (clearBufferOnFail) {
writeBuffer.clear();
currentWriteBufferSize = 0;
} else {
// the write buffer was adjusted by processBatchOfPuts
currentWriteBufferSize = 0;
for (Put aPut : writeBuffer) {
currentWriteBufferSize += aPut.heapSize();
}
}
}
}
connection是一个virtual class,HConnection,默认实现是HConnectionImplementation,从注释可以知道这个connection是用来"Encapsulates connection to zookeeper and regionservers." 我们追踪processBatchOfPuts这个实现,开辟results数组记录那些put是成功的,成功的put之后会被remove出去。底层还是调用了processBatch这个过程。
public void processBatchOfPuts(List<Put> list,
final byte[] tableName,
ExecutorService pool) throws IOException {
Object[] results = new Object[list.size()];
try {
processBatch((List) list, tableName, pool, results);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IOException(e);
} finally {
// mutate list so that it is empty for complete success, or contains only failed records
// results are returned in the same order as the requests in list
// walk the list backwards, so we can remove from list without impacting the indexes of earlier members
for (int i = results.length - 1; i>=0; i--) {
if (results[i] instanceof Result) {
// successful Puts are removed from the list here.
list.remove(i);
}
}
}
}
processBatch代码比较冗长,大致意思如下:
- prcessBatch会尝试执行多次,从配置hbase.client.retries.number获得,默认10
- 每次重试之前都会sleep一段时间,这个时间从getPauseTime获得,是个大致指数退避的算法。
- 根据每个row获得对应的HServerAddress,以HServerAddress为key将相同地址请求放在HashMap,HashMap类型是Map<HServerAddress, MultiAction>
- 将每个MultiAction放到ExecutorService里面得到future对象,然后阻塞等待future对象返回并且逐个检查。
- 处理每个请求返回的结果,检查过程比较麻烦没有仔细阅读。
我们最关心的问题就是这个ExecutorService的线程池是什么,从HTable里面我们可以找到答案
- new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, maxThreads, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), new DaemonThreadFactory());
- maxThreads从属性hbase.htable.threads.max获得。
20. asynchbase
https://github.com/stumbleupon/asynchbase
- asynchbase和HTable的性能对比 http://www.tsunanet.net/~tsuna/asynchbase/benchmark/viz.html
- OpenTSDB is a distributed, scalable Time Series Database (TSDB) http://opentsdb.net/index.html
从看asynchbase介绍来看,我猜想asynchbase用在MR范围还是有限的。
- asynchbase就是一个异步client,能够很好地解决一个app里面对于hbase有很多个连接的场景。
- 但是在MR里面,拿我们现在的HourlyProcedure来说,每次get都是一个同步过程,一定要取回结果才能够进行下一步的操作。整个MR框架就限制了异步client的作用。
- asynchbase现在使用的场景应该是OpenTSDB,因为没有MR框架限制,所以异步client可以工作很好。
#note@2012-12-10: code/java/asynchbase下面有一些使用的示例代码,并且在自己的fast-hbase-rest里面也使用了asynchbase. 使用还是比较方便的。 实现上asynchbase没有使用任何org.apache.hbase的代码,从头完成了自己的协议访问,这个可以从HBaseClient的构造参数可以看到,在里面没有使用configuration, 而是直接传入quorumSpec就是zookeeper的地址。
#note: 关于Deferred实现有点出乎自己的意料
https://github.com/OpenTSDB/asynchbase/issues/72
测试代码可以参考 code on github, 在Get添加Callback之前会检查结果是否已经获取到。如果已经获取的话,那么会在当前的线程就执行callback
=== Question
Apology at first because this question should be raise in groups. But since the project has no groups or mail list, so I have to resort to the Github issue.
What I wonder is that, is asynchbase using Deferred concept in the right way. I raise a GetRequest first, then get the Deferred object, then bind the callback to the object. However I guess sometimes this way won't work. Let me take the following extremely case for example.
val deferred = client.get(request) / wait or hang for a LONG time. deferred addCallback { / process. }
Since we add callback to the chain too later, I guess asynchbase engine will not execute the callback, will it?
I think the right form should be the following instead of above
client.get(request, new Callback {});
and before launch the operation, engine has to make sure the callback already bind to the operation.
Recently I learn Twitter's finagle, they bring up the concept of Future much like Deferred. However the biggest difference is Future binds to service, and Deferred binds to request.
=== Answer
Try and see by yourself: it works.
The reason it works is that if you add a Callback on a Deferred that already has its result available, then the Callback will be invoked right away, with that result in argument.
So everything is fine :)
21. clock skew
如果region server和master的时间偏差太大的话,会造成region server启动失败
at sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(NativeConstructorAccessorImpl.java:39)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.newInstance(DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl.java:27)
at java.lang.reflect.Constructor.newInstance(Constructor.java:513)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RemoteException.instantiateException(RemoteException.java:95)
at org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RemoteException.unwrapRemoteException(RemoteException.java:79)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer.reportForDuty(HRegionServer.java:1506)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer.tryReportForDuty(HRegionServer.java:1470)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer.run(HRegionServer.java:563)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:662)
Caused by: org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RemoteException: org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ClockOutOfSyncException: Server s3,60020,1304927875246 has been rejected; Reported time is too far out of sync with master. Time difference of 41450ms > max allowed of 30000ms
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.master.ServerManager.checkClockSkew(ServerManager.java:181)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.master.ServerManager.regionServerStartup(ServerManager.java:129)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.master.HMaster.regionServerStartup(HMaster.java:613)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:39)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HBaseRPC$Server.call(HBaseRPC.java:570)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HBaseServer$Handler.run(HBaseServer.java:1039)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HBaseClient.call(HBaseClient.java:771)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HBaseRPC$Invoker.invoke(HBaseRPC.java:257)
at $Proxy5.regionServerStartup(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer.reportForDuty(HRegionServer.java:1502)
通常出现这个问题的原因是因为ntp没有正常工作导致本地时钟出现偏差(clock skew).这个参数通过 hbase.master.maxclockskew 来配置,默认是30000(ms)也就是30s.
为什么hbase要规定region server和master时间同步呢?这篇文章给出了解释我觉得比较靠谱. hbase/hypertable集群启动需要进行时间同步原因?
这里假设一个range从rs1到rs2,并且rs1当前时间是6:00,rs2的当前时间是5:00,并且rs1上在5:59的时候写入数据<k1, v1, 5:59>,之后该range迁移到了rs2了,并且rs2已经能够向外界提供服务了,在5:10来了个对k1的修改请求,将k1对应的值改成v2,这时rs2将写入<k1, v2, 5:10>。这时如果来了对k1的查询请求的话,rs2将返回<k1, v1>,但实际上这已经是旧的数据了。
rs2最近写入的数据是v2,而接下来如果从rs2查询"latest"的数据的话返回的是v1。
22. hbase join
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/11327316/how-to-join-tables-in-hbase
其实对于join来说无非三种:
- sort join 两路排序,之后进行merge。
- loop join 没有任何排序,直接循环匹配。
- hash join 遍历一路的时候去查另外一路。
对于MR来说,个人认为sort join通常是效率最高的方式,而hash join次之(hbase的read效率不是很高)。