Web Search for a Planet
Table of Contents
http://research.google.com/archive/googlecluster.html @ 2003
除了软件架构之外,还提到了硬件上的选择和优化
1. Google architecture overview
In summary, Google clusters follow three key design principles:
- Software reliability. We eschew fault-tol-erant hardware features such as redun-dant power supplies, a redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID), and high-quality components, instead focusing on tolerating failures in software.(不在硬件层面保证可靠性,相反在软件层面来处理这些问题)
- Use replication for better request through-put and availability. Because machines are inherently unreliable, we replicate each of our internal services across many machines. Because we already replicate services across multiple machines to obtain sufficient capacity, this type of fault tolerance almost comes for free.(通过replication来获得高吞吐以及可用性)
- Price/performance beats peak performance. We purchase the CPU generation that currently gives the best performance per unit price, not the CPUs that give the best absolute performance. (关注price/performance而不仅仅是关注performance)
- Using commodity PCs reduces the cost of computation. As a result, we can afford to use more computational resources per query, employ more expensive techniques in our ranking algorithm, or search a larger index of documents(使用廉价PC来构建集群)
2. Leveraging commodity parts
- Google’s racks consist of 40 to 80 x86-based servers mounted on either side of a custom made rack (each side of the rack contains twenty 20u or forty 1u servers).(每个rack上面有40-80台x86服务器,rack每一面可以放下20个2u或者是40个1u服务器)
- Our focus on price/performance favors servers that resemble mid-range desktop PCs in terms of their com-ponents, except for the choice of large disk drives.(主要使用普通的桌面PC但是换成大容量硬盘)
- Several CPU generations are in active service, ranging from single-processor 533- MHz Intel-Celeron-based servers to dual 1.4-GHz Intel Pentium III servers.(CPU有从533MHz的赛扬到1.4GHz的奔腾)
- Each server contains one or more integrated drive elec- tronics (IDE) drives, each holding 80 Gbytes.(使用80GB的IDE磁盘驱动器)
- The servers on each side of a rack interconnect via a 100-Mbps Ethernet switch that has one or two gigabit uplinks to a core gigabit switch that connects all racks together(rack一侧的机器之间通过100Mbps的以太交换机,rack之间交换机使用千兆网卡)
- Our ultimate selection criterion is cost per query, expressed as the sum of capital expense (with depreciation) and operating costs (host-ing, system administration, and repairs) divid-ed by performance.(费用方面包括资本开销包括折旧,以及运维开销)
- Realistically, a server will not last beyond two or three years, because of its disparity in performance when compared to newer machines. Machines older than three years are so much slower than current-gener-ation machines that it is difficult to achieve proper load distribution and configuration in clusters containing both types.(但是实际情况是,一台服务器可能在2-3年之后相比更新的机器性能就有非常大的差距,因此对于一台服务器的寿命而言就是2-3年的时间)
- Given the rel-atively short amortization period, the equip-ment cost figures prominently in the overall cost equation.(考虑到这点因素之后,因此开销主要还是集中在设备上)
- For example, in late 2002 a rack of 88 dual-CPU 2-GHz Intel Xeon servers with 2 Gbytes of RAM and an 80-Gbyte hard disk was offered on RackSaver.com for around $278,000. This figure translates into a monthly capital cost of $7,700 per rack over three years. (2002年一个rack上面88个双核CPU的Xeon服务器,配备2G内存以及80GB的磁盘在racksaver.com上面大概需要278000美元,平均每年7700美元).
- The relative importance of equipment cost makes traditional server solutions less appeal-ing for our problem because they increase per-formance but decrease the price/performance. (一些传统的服务器解决方案对于我们来说缺乏吸引力,主要是因为虽然增加了性能,但是降低了performance/price)
- For example, four-processor motherboards are expensive, and because our application paral-lelizes very well, such a motherboard doesn’t recoup its additional cost with better perfor-mance. (比如对于能够支持4个CPU的主板,因为我们自身程序并行性已经非常好了,所以额外的开销并没有带来更好的性能)
- Similarly, although SCSI disks are faster and more reliable, they typically cost two or three times as much as an equal-capac-ity IDE drive.(而对于SCSI磁盘来说虽然更快并且并且更加可靠,但是价钱是同样大小的IDE的2-3倍)
- The cost advantages of using inexpensive, PC-based clusters over high-end multi-processor servers can be quite substantial, at least for a highly parallelizable application like ours.( 使用PC-based这样的集群而不是使用高端的多处理器server带来的好处是非常明显的,尤其是对于并行程度非常高的应用程序 )
- The example $278,000 rack contains 176 2-GHz Xeon CPUs, 176 Gbytes of RAM, and 7 Tbytes of disk space.
- In com-parison, a typical x86-based server contains eight 2-GHz Xeon CPUs, 64 Gbytes of RAM, and 8 Tbytes of disk space; it costs about $758,000.(这个是高端服务器的报价,上面是之前提到的集群)
- Operating thousands of mid-range PCs instead of a few high-end multiprocessor servers incurs significant system administra-tion and repair costs.(对于使用PC集群带来的唯一坏处就是机器非常多而故障率非常高,带来的管理成本和维修成本)
- However, for a relative-ly homogenous application like Google, where most servers run one of very few appli-cations, these costs are manageable.(但是大部分的应用都是同构的,而且每个server上面只是运行有限的几个程序)
- Assum-ing tools to install and upgrade software on groups of machines are available, the time and cost to maintain 1,000 servers isn’t much more than the cost of maintaining 100 servers because all machines have identical configu-rations. (同时使用相同的配置以及自动化部署可以在一定程度上解决这个问题)
- Similarly, the cost of monitoring a cluster using a scalable application-monitor-ing system does not increase greatly with clus-ter size.(对于集群的监控通过可以扩展的监控系统完成)
- Furthermore, we can keep repair costs reasonably low by batching repairs and ensur-ing that we can easily swap out components with the highest failure rates, such as disks and power supplies.(可以批量地进行部件维修。而且因为软件本身就是对于hardward failure是可容忍的,所以替换一些出问题的组件也非常容易)
3. The power problem
4. Hardware-level application characteristics
- Examining various architectural characteris-tics of our application helps illustrate which hardware platforms will provide the best price/performance for our query-serving sys-tem.(分析应用程序的一些架构上面的特征,来解释什么硬件可以为查询系统提供更好的性价比)
- We’ll concentrate on the characteristics of the index server, the component of our infra-structure whose price/performance most heav-ily impacts overall price/performance. (主要是针对index server这个部件来进行分析,因为这个部分对于性价比的影响非常大)
- The main activity in the index server consists of decoding compressed information in the inverted index and finding matches against a set of documents that could satisfy a query. (index server主要的功能就是decode反向索引信息然后做一些聚合操作)
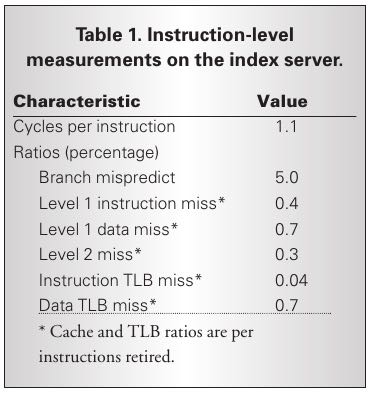
- The application has a moderately high CPI, considering that the Pentium III is capable of issuing three instructions per cycle. 考虑到P3能够一个cycle执行3条指令,现在每个cycle执行1.1条指令算是相对比较高的CPI了。
- We expect such behavior, considering that the applica-tion traverses dynamic data structures and that control flow is data dependent, creating a sig-nificant number of difficult-to-predict branches.(对于这个CPI的解释是因为进行遍历了太多动态的数据结构并且有数据以依赖,造成了非常多难以预测的分支)
- In fact, the same workload running on the newer Pentium 4 processor exhibits nearly twice the CPI and approximately the same branch prediction performance, even though the Pentium 4 can issue more instruc-tions concurrently and has superior branch prediction logic.(事实上,相同的workload在新的P4上面运行产生了2倍的CPI以及相同的分支条转性能,虽然P4能够同时执行更多的指令并且有更好的分支预测)
- In essence, there isn’t that much exploitable instruction-level parallelism (ILP) in the workload. Our measurements suggest that the level of aggressive out-of-order, speculative execution present in mod-ern processors is already beyond the point of diminishing performance returns for such programs. (所以说白了workload的ILP没有那么高,因此测试建议现代处理器里面的乱序执行以及推测执行对我们的应用程序没有太多的用途)
- A more profitable way to exploit parallelism for applications such as the index server is to leverage the trivially parallelizable computa-tion.(所以探索并行性更经济的做法是利用这些本身就是可并行的计算)
- Exploiting such abundant thread-level parallelism at the microarchitecture level appears equally promising. Both simultaneous multithreading (SMT) and chip multiproces-sor (CMP) architectures target thread-level parallelism and should improve the perfor-mance of many of our servers.(另外在微处理器架构层面提升线程级别的并行性还是更加有意义的,SMT或者是CMP似乎都能够提高性能)
- Some early experiments with a dual-context (SMT) Intel Xeon processor show more than a 30 percent performance improvement over a single-con-text setup. This speedup is at the upper bound of improvements reported by Intel for their SMT implementation.(早期的一些SMT实验发现能够提升30%的性能,但是似乎这个加速是存在上限的)
- We believe that the potential for CMP sys-tems is even greater. CMP designs, such as Hydra and Piranha seem especially promis-ing.(我们相信CMP是更加经济的做法)
- In these designs, multiple (four to eight) simpler, in-order, short-pipeline cores replace a complex high-performance core. 设计上使用4-8个非常简单的,顺序执行,短流水线的核
- The penal-ties of in-order execution should be minor given how little ILP our application yields,(in-order执行带来的损失就是对于稍微降低ILP)
- and shorter pipelines would reduce or elimi-nate branch mispredict penalties. 短流水线却能够在一定程度上减少分支预测错误惩罚
- The avail-able thread-level parallelism should allow near-linear speedup with the number of cores, and a shared L2 cache of reasonable size would speed up interprocessor communication.(始终这种线程级别的并行能够基本达到线性加速,而使用合理大小的共享L2可以加快处理器之间的通信)