systemtap
Table of Contents
常用链接:
- SystemTap http://sourceware.org/systemtap/ 文档 http://sourceware.org/systemtap/documentation.html
- Linux 自检和 SystemTap http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-systemtap/
- IBM Redbooks | SystemTap: Instrumenting the Linux Kernel for Analyzing Performance and Functional Problems
- Architecture of systemtap a Linux trace probe tool http://sourceware.org/systemtap/archpaper.pdf
- Dynamic Instrumentation of Production Systems http://static.usenix.org/event/usenix04/tech/general/full_papers/cantrill/cantrill_html/
1. Getting Started
systemtap的工作原理是使用linux提供的kprobe接口,将用户需要观测linux系统的行为转换成为c,然后结合kprobe编译成为kernel object然后运行。
systemtap使用一种触发式的工作方式,通过安装探针(probe)来监控系统的行为,一旦探针事件出现的话就会触发对应的代码。
代码使用自己定义的语言,和C语言非常类似。
准备过程是下面这样的:
- stap 流程从将脚本转换成解析树开始 (pass 1)
- 然后使用细化(elaboration)步骤 (pass 2) 中关于当前运行的内核的符号信息解析符号
- 接下来转换流程将解析树转换成 C 源代码 (pass 3) 并使用解析后的信息和 tapset 脚本(SystemTap 定义的库,包含有用的功能)
- stap 的最后步骤是构造使用本地内核模块构建进程的内核模块 (pass 4)。
执行过程是下面这样的:
- staprun 负责启动kernel object
- stapio 负责收集kernel object的输出
- 执行期间中断的话将执行清除进程,卸载模块并退出所有相关的实用程序
一个使用systemtap的简单例子
[dirlt@umeng-ubuntu-pc] > sudo stap -ve 'probe begin { log("hello world") exit() }'
Pass 1: parsed user script and 76 library script(s) using 92476virt/22592res/2616shr kb, in 80usr/0sys/85real ms.
Pass 2: analyzed script: 1 probe(s), 2 function(s), 0 embed(s), 0 global(s) using 93000virt/23472res/2816shr kb, in 0usr/0sys/4real
ms.
Pass 3: translated to C into "/tmp/stapbx8Gpk/stap_7703b9bd08bd359932cf8da12019f6d8_813.c" using 93000virt/23628res/2964shr kb, in 0
usr/0sys/0real ms.
Pass 4: compiled C into "stap_7703b9bd08bd359932cf8da12019f6d8_813.ko" in 3240usr/510sys/4048real ms.
Pass 5: starting run.
hello world
Pass 5: run completed in 10usr/10sys/600real ms.
[dirlt@umeng-ubuntu-pc] > sudo stap -ve 'probe begin { log("hello world") exit() }'
Pass 1: parsed user script and 76 library script(s) using 92476virt/22592res/2616shr kb, in 80usr/10sys/85real ms.
Pass 2: analyzed script: 1 probe(s), 2 function(s), 0 embed(s), 0 global(s) using 93000virt/23472res/2816shr kb, in 0usr/0sys/4real
ms.
Pass 3: using cached /home/dirlt/.systemtap/cache/77/stap_7703b9bd08bd359932cf8da12019f6d8_813.c
Pass 4: using cached /home/dirlt/.systemtap/cache/77/stap_7703b9bd08bd359932cf8da12019f6d8_813.ko
Pass 5: starting run.
hello world
Pass 5: run completed in 0usr/10sys/586real ms.
可以看到在第二次运行的时候systemtap会去读取缓存内容。
2. Architecture of systemtap a Linux trace probe tool
2.1. Systemtap processing steps
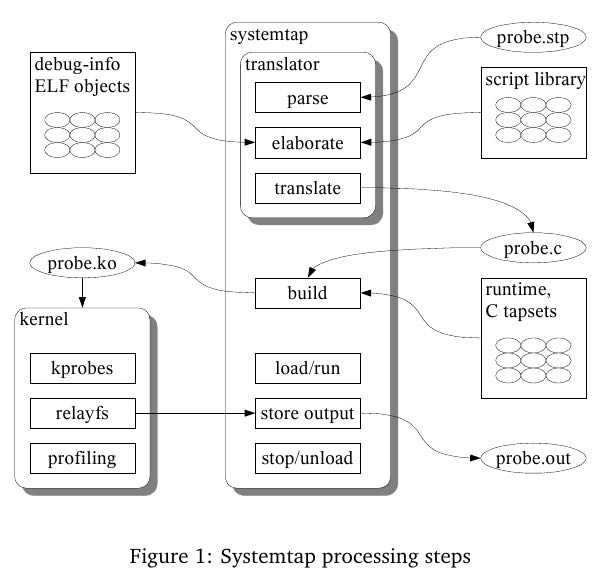
Probe language
- The language describes an association of handler subroutines with probe points. 类似AWK的工作方式,绑定一些handle到probe points上面
- Probe points are abstract names given to identify a particular place in kernel/user code, or a particular event (timers, counters) that may occur at any time. (所谓探测点是用来识别内核或者是用户代码的一些位置,或者是某些事件的发生)
- Handlers are subroutines written in the script language, which are run whenever the probe points are hit.(而handler就是当探测点出发的时候执行的过程)
- The language resembles dtrace’s “D”, itself inspired by the old UNIX tool awk(语言名字叫做D引用dtrace,非常类似awk的语言)
- These are simplified from C, lacking types, declarations, and most indirection 类似C但是没有类型和声明以及间接引用
- but adding associative arrays and simplified string process-ing. 关联数组实现
- The language includes some extensions to interoperate with the target software being instrumented, in order to refer to its data and program state. 增加扩展用来引用系统或者是应用程序特定的数据。
Elaboration
- Elaboration is a processing phase that analyzes the input script, and resolves any needed symbolic references to the kernel, user programs, or other any “tapsets”. (这个过程解析符号交叉引用,包括内核,用户程序以及tapset)
- Tapsets are libraries of script or C code used to extend the capability of a basic script(tapset类似library,有D实现也有C扩展)
- Elaboration is analogous to linking an object file with needed libraries, turn them into a self-contained executable.(类似与链接过程)
- References to kernel data such as function parameters, local and global variables, functions, source locations, all need to be resolved to actual run-time addresses.(对于引用kenel或者是可执行文件的符号都是在run之前就完成解析的)
- This is most rigorously done by processing the DWARF debugging information emitted by the compiler, in the same way as an ordinary debugger would(通过处理DWARF debugging信息来完成的)
- However, such debug data processing is transformed into an executable form ahead of time, so that during actual probe execution, no explicit decoding is necessary.(但是这些debug数据因为是静态的,所以可以在run之前完成)
Translation
- Once an entire set of probe functions is processed through the elaboration stage, they are translated to a quantity of C code.(生成C代码)
- Each systemtap construct is expanded to a block of C that includes whatever locking and safety checks are necessary.
- Control-flow constructs translate to include runaway-prevention logic.
- Each variable shared amongst probes is mapped to an appropriate static declaration, and accesses are protected by locks.(全局变量生成static并且通过lock来保护)
- Each group of local variables is placed into a synthetic call frame structure that keeps them off the tiny real kernel stacks.
- Probe handlers are wrapped by an interface function which uses whatever probe point registration API is appropriate. (所有的probe handler都被包装成为function然后注册到probe point回调,但是方式有所不同)
- For location type probe points targeting the kernel, this generally uses kprobes.(如果是内核探测点的话,那么使用kprobe)
- Where the target software is user-level, probe points would need to be inserted into specific processes’ executable segments, using a mechanism yet to be specified.(如果是用户程序探测点的话,那么需要修改进程内存)
- When complete, the generated C code is compiled, and linked with the runtime, into a stand-alone kernel module. For security reasons, the module may be cryptographically signed, so that it may be archived and later reused here, or on another computer without a compiler installed.(编译成为ko模块,并且签名做cache)
Execution
- To run the probes, the systemtap driver program simply loads the kernel module using insmod. 使用insmod安装ko模块
- The module will initialize itself, insert the probes, then sit back and let the probe handlers be triggered by the system to collect and pass data. It will eventually remove the probes at unload time.(模块初始化之后安装probe然后等待handle触发,在unload的时候会将probes全部移除)
- When a probe is hit, the associated handler routine takes over the processor, suspending the target software briefly. When all handlers for that probe point have been executed, the target program resumes.(probe hit之后handler会执行,等待所有的handler执行完成之后目标程序才开始运行,因此最好不用hold住handler)
- The probe run concludes when the user sends an interrupt to the driver, or when the probe script runs an exit primitive. (This primitive might simply send a SIGINT to the running user-level driver process.) 通过发起信号结束
2.2. Programming
A systemtap script file has the suffix “.stp”
A script file is a sequence of top-level constructs, of which there are three types: 下面这些元素组成
- probe definitions, 探针定义
- auxiliary function definitions, 辅助函数定义
- and global variable declarations. 全局变量
- These may occur in any order, and forward references are permitted. 可以向前引用
Multiple probe handlers may execute concurrently on a multiprocessor. Multiple probe definitions may end up referring to the same event or program location (多个probe handler可能会在多个CPU上同时执行,并且不同的probe def可能引用到program的相同位置,因此需要注意多线程问题)
A script may make references to an identifier defined elsewhere in library of script tapsets. Such a cross-reference causes the entire tapset file providing the definition to be merged into the elaborated script, as if it was simply concatenated. (如果引用其他script变量的话,那么elaboration阶段会将引用的script全部包含进来,简单地看就像是合并)
Fatal errors that occur during script execution cause a winddown of activity associated with the systemtap script, and an early abort. Running out of memory, dividing by zero, exceeding an operation count limit, calling too many nested functions, are just a few types of fatal errors(运行中如果出现问题的话会使得script提前中止)
2.2.1. Probe points
A probe definition gives probe points in a comma-separated list, and an associated action in the form of a statement block.(使用,分割多个probe points)
Each probe point specification has a “dotted-functor” syntax such as kernel.function("foo").return(probe point通过.来表示层级)
- kernel or module("foo") kernel或者是foo.ko模块
- functions("fn") / function("fn@filename") / function("fn@filename:lineno") / function(0x1f) PC
- .callees 可以指定这个fn所有调用的函数
- .return fn返回时候触发,默认是.entry
- statement("fn") / statement("fn@filename") / statement("fn@filename:lineno") / statement(0x1f) PC
- .relative(0x1f) 偏移定位
- .label("need_resched") 标签定位
- events 主要指抽象事件,和kernel或者是program无关。
下面是一些示例代码
kernel.function("sys_read").return
a return probe on the named function.
module("ext3").function("*@fs/ext3/inode.c")
every function in the named source file, a part of ext3fs
kernel.function("kmalloc").callees
every function known statically to be callable from kmalloc
module("usb-storage").statement(0x0233)
the given address, which must be at an instruction boundary
kernel.function(0xffffffff802202dc).return
a return probe on whichever function that contains the given address
2.3. Lower layer issues
Data collected from systemtap in the kernel must somehow be transmitted to userspace. This transport must have high performance and minimal performance impact on the monitored system. 在内核态收集的数据必须发送到用户态空间,这个传输过程必须满足高性能。