Java Native Interface: Programmer's Guide and Specification
Table of Contents
UPDATE@202301: 这个PDF 318页,我也是JNI新手,估计当时看的也是稀里糊涂的。
1. Introduction
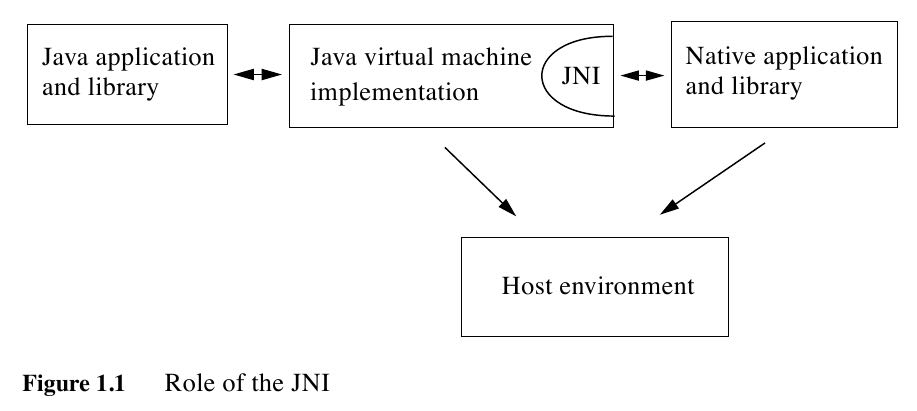
The JNI is designed to handle situations where you need to combine Java applications with native code. As a two-way interface, the JNI can support two types of native code: native libraries and native applications. (允许相互调用)
- You can use the JNI to write native methods that allow Java applications to call functions implemented in native libraries. (native libraries通过native methods被JVM调用)
- The JNI supports an invocation interface that allows you to embed a Java vir-tual machine implementation into native applications.(native applications通过invocation interface调用JVM)
下面是一些JNI的代替方案(主要都是通过进程间通信来完成的)
- A Java application may communicate with a native application through a TCP/IP connection or through other inter-process communication (IPC) mechanisms.
- A Java application may connect to a legacy database through the JDBC API.
- A Java application may take advantage of distributed object technologies such as the Java IDL API.
下面是一些JNI比较适合的场景
- The Java API might not support certain host-dependent features needed by an application. An application may want to perform, for example, special file operations that are not supported by the Java API, yet it is both cumbersome and inefficient to manipulate files through another process.(在一些host上面非常特殊的操作)
- You may want to access an existing native library and are not willing to pay for the overhead of copying and transmitting data across different processes. Loading the native library in the same process is much more efficient.(进程之间通信需要拷贝传输大量的数据)
- Having an application span multiple processes could result in unacceptable memory footprint. This is typically true if these processes need to reside on the same client machine. Loading a native library into the existing process hosting the application requires less system resources than starting a new pro-cess and loading the library into that process.(单独的进程会存在相当的overhead)
- You may want to implement a small portion of time-critical code in a lower-level language, such as assembly. If a 3D-intensive application spends most of its time in graphics rendering, you may find it necessary to write the core por-tion of a graphics library in assembly code to achieve maximum performance.(控制底层提高性能效率)
2. Getting Started
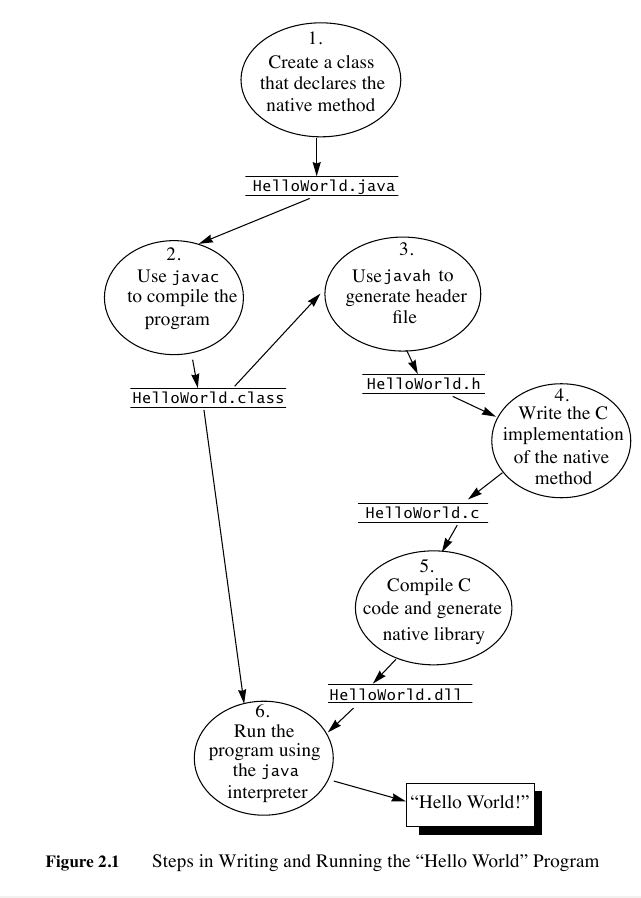
主要介绍的是native methods编写,JVM通过so来调用native methods.这里给出一个无参native mthods例子。
- javac Hello.java 生成 Hello.class
- javah -jni Hello 生成 Hello.h
- 编写 Hello.cc 使用 Hello.h 生成 libHello.so # g++ Hello.cc -fPIC -o libHello.so -shared -I$JAVA_HOME/include
- 将 libHello.so 加入到library path.
- 然后 java Hello 启动
2.1. Hello.java
/* coding:utf-8
* Copyright (C) dirlt
*/
public class Hello {
private static native void run();
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.loadLibrary("Hello");
run();
}
}
2.2. Hello.h
/* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE - it is machine generated */ #include <jni.h> /* Header for class Hello */ #ifndef _Included_Hello #define _Included_Hello #ifdef __cplusplus extern "C" { #endif /* * Class: Hello * Method: run * Signature: ()V */ JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_Hello_run (JNIEnv *, jclass); #ifdef __cplusplus } #endif #endif
2.3. Hello.cc
/* coding:utf-8 * Copyright (C) dirlt */ #include <cstdio> #include "Hello.h" JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_Hello_run (JNIEnv * env, jclass cls) printf("Hello,World\n"); }
3. Basic Types, Strings, and Arrays
- The static initializer calls the System.loadLibrary method to load a native library called Prompt.
- 使用System.loadLibrary来载入动态库
- The JNIEXPORT and JNICALL macros (defined in the jni.h header file) ensure that this function is exported from the native library and C compilers generate code with the correct calling convention for this function
- JNIEXPORT用来导出函数声明,JNICALL用来规定函数调用方式
- The name of the C function is formed by concatenating the “Java_” prefix, the class name, and the method name.
- Java_作为前缀,然后是class name,然后是method_name
- The first parameter, the JNIEnv interface pointer, points to a location that contains a pointer to a function table.
- JNIEnv定义了JNI所有可以访问JVM对象的接口方法
- 这个结构在$JAVA_HOME/include/jni.h里面有定义
- The second argument to an instance native method is a reference to the object on which the method is invoked, similar to the this pointer in C++. The second argument to a static native method is a reference to the class in which the method is defined.
- 如果是static方法的话,那么参数是指class对象
- 如果不是static方法的话,那么参数是指object对象
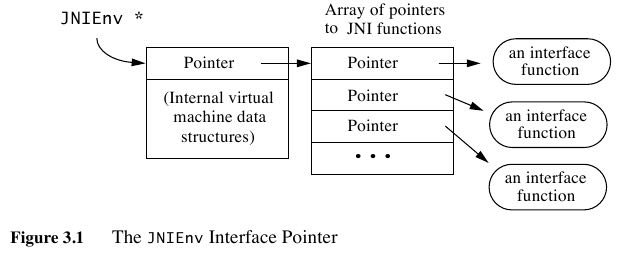
可以看到在pointer下面还有一个internal VM数据块,这个是线程级别的私有数据跟在pointer之后,可以通过指针偏移进行访问
对于类型还说分为primitive和reference两种类型,reference type都是opaque pointer获取数据必须通过JNIEnv接口提供的方法才能够获得。
至于具体类型是pritmitive还是reference的话,可以通过阅读jni.h和jni_md.h来判断。primitive type只有下面几种(defined in jni_md.h)
#ifndef _JAVASOFT_JNI_MD_H_ #define _JAVASOFT_JNI_MD_H_ #define JNIEXPORT #define JNIIMPORT #define JNICALL typedef int jint; #ifdef _LP64 /* 64-bit Solaris */ typedef long jlong; #else typedef long long jlong; #endif typedef signed char jbyte; #endif /* !_JAVASOFT_JNI_MD_H_ */
4. Fields and Methods
Field操作:
- GetObjectClass获取object所属的class对象,类型是jclass. 如果是本地静态方法的话,那么传入参数应该就是class对象
- GetFieldID/GetStaticFieldID根据field descriptor获取field id,类型是jfieldID.
- field descriptor字符串可以通过javap -s -p <class>来获取
- 字符串称为JNI field descriptor
- I int
- F float
- D double
- Z boolean
- / 代替package name中的.
- [ array
- L reference
- V void
- 比如如果是String[]的话,那么就是"[Ljava/lang/String;"
- Get<type>Field/GetStatic<type>Field获取field data.
- Set<type>Field/GetStatic<type>Field设置field data.
Method操作:
- 获取jclass
- GetMethodID/GetStaticMethodID根据method descriptor获取method id,类型是jmethodID.
- method descriptor同样可以使用javap来获得
- 字符串形式如下"(arg types)return type"
- 比如如果是void f(String arg),那么就是"(Ljava/lang/String;)V"
- Call<Type>Method/CallStatic<Type>Method来调用method.
- 如果调用superclass method的话,那么调用CallNonvirtual<Type>Method.
- 构造函数的名称是"<init>" (返回参数是void类型)
- NewObject分配空间并且调用构造函数
- AllocObject只是开辟空间需要自己调用构造函数
Cache fieldID/methodID:
- 每次查找ID的代价非常大,通过cache可以避免
- 第一种方法是每次查找的时候都判断是否为null,如果为null那么查找然后缓存起来。
- 第二种方法是在类static区域调用初始化函数,初始化函数一次性获取所有的ID然后缓存。
- 可以认为第一种方法就是lazy evaluation.
Let us start by comparing the cost of Java/native calls with the cost of Java/Java calls. Java/native calls are potentially slower than Java/Java calls for the fol-lowing reasons: (Java/Java calls和Java/native calls的对比,Java/native calls通常更慢):
- Native methods most likely follow a different calling convention than that used by Java/Java calls inside the Java virtual machine implementation. As a result, the virtual machine must perform additional operations to build argu-ments and set up the stack frame before jumping to a native method entry point.(额外操作来建立stack frame调用native method)
- It is common for the virtual machine to inline method calls. Inlining Java/native calls is a lot harder than inlining Java/Java calls. (inline方面Java/Java calls更容易做)
The overhead of field access using the JNI lies in the cost of calling through the JNIEnv. Rather than directly dereferencing objects, the native code has to per- form a C function call which in turn dereferences the object. The function call is necessary because it isolates the native code from the internal object representa-tion maintained by the virtual machine implementation. The JNI field access over-head is typically negligible because a function call takes only a few cycles.(字段访问开销主要是通过一次得到ID间接访问造成的,但是这样带来的收益是能够将内部object表示不暴露出来,索性的是带来的开销并不大)
5. Local and Gloabl References
reference和GC非常相关,决定了哪些对象作用域多大以及生命周期多长:
- The JNI supports three kinds of opaque references: local references, global references, and weak global references.
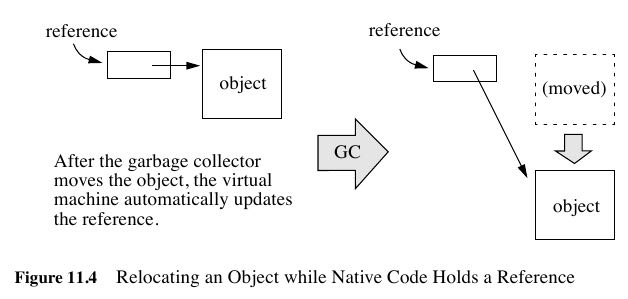
- Local and global references have different lifetimes. Local references are automatically freed, whereas global and weak global references remain valid until they are freed by the programmer.
- A local or global reference keeps the referenced object from being garbage collected. A weak global reference, on the other hand, allows the referenced object to be garbage collected.
分为三类references:
- local 对象超过函数作用域之后就会自动释放
- Why do you want to delete local references explicitly if the virtual machine automatically frees them after native methods return? A local reference keeps the referenced object from being garbage collected until the local reference is invali-dated.
- 但是也可以显示标记不需要这个对象,这样可以减少无用对象的持有。使用DeleteLocalRef来标记。(似乎对于每一个native method最多支持16个local reference ???)
- NewLocalRef/DeleteLocalRef.
- JDK1.2以上有另外的方法支持很多local reference
- EnsureLocalCapacity 确保这个frame至少之后可以分配多少个local ref
- PushLocalFrame/PopLocalFrame 新建和释放一个local frame.这样可以开辟更多的local ref.
- global 对象生命周期直到程序结束
- NewGlobalRef/DeleteGlobalRef
- weak global 和global非常类似,但是可以通过操作标记这个对象不在需要然后被GC
- NewGlobalWeakRef/DeleteGlobalWeakRef
- IsSameObject 能够判断两个reference是否相同
- 如果传入NULL的话表示,对于local和lglobal表示对象是否为null,对于weak global来说的话判断这个对象是否依然指向一个lived object而没有被回收。
6. Exceptions
- Throw 抛出已有异常
- ThrowNew 创建异常对象抛出
- ExceptionOccurred 获得pending exception.
- ExceptionCheck 检查是否存在pending exception.
- ExceptionDescribe 打印pening exception描述信息
- ExceptionClear 清除pending exception状态
- FatalError 打印fatal信息
JNI programmers may deal with an exception in two ways:
- The native method may choose to return immediately, causing the exception to be thrown in the code that initiated the native method call.
- The native code may clear the exception by calling ExceptionClear and then execute its own exception-handling code.
It is extremely important to check, handle, and clear a pending exception before calling any subsequent JNI functions.
native code如果不处理异常的话,可以直接返回交给caller来处理异常。如果是自己处理异常的话,获得具体异常之后最好立刻清除状态,然后做后续操作。
Calling most JNI functions with a pending exception leads to undefined results. The following is the complete list of JNI functions that can be called safely when there is a pending exception:
- ExceptionOccurred
- ExceptionDescribe
- ExceptionClear
- ExceptionCheck
- ReleaseStringChars
- ReleaseStringUTFchars
- ReleaseStringCritical
- Release<Type>ArrayElements
- ReleasePrimitiveArrayCritical
- DeleteLocalRef
- DeleteGlobalRef
- DeleteWeakGlobalRef
- MonitorExit
7. The Invocation Interface
/* coding:utf-8 * Copyright (C) dirlt */ #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <jni.h> static JNIEnv* env; static JavaVM* jvm; void destroy() { if (env->ExceptionOccurred()) { env->ExceptionDescribe(); } jvm->DestroyJavaVM(); } int main() { JavaVMInitArgs vm_args; JavaVMOption options[1]; options[0].optionString = "-Djava.class.path=."; vm_args.version = JNI_VERSION_1_6; vm_args.options = options; vm_args.nOptions = 1; vm_args.ignoreUnrecognized = JNI_TRUE; /* Create the Java VM */ jint res = JNI_CreateJavaVM(&jvm, (void**)&env, &vm_args); if (res < 0) { // can't create jvm. fprintf(stderr, "Can't create Java VM\n"); exit(1); } jclass cls = env->FindClass("Hello"); if (cls == NULL) { // can't find class. destroy(); } jmethodID mid = env->GetStaticMethodID(cls, "main", "([Ljava/lang/String;)V"); if (mid == NULL) { // no main method. destroy(); } jstring jstr = env->NewStringUTF(" from C!"); if (jstr == NULL) { destroy(); } jclass stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String"); jobjectArray args = env->NewObjectArray(1, stringClass, jstr); if (args == NULL) { destroy(); } env->CallStaticVoidMethod(cls, mid, args); destroy(); }
➜ ~ g++ Hello.cc -I$JAVA_HOME/include -L$JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/amd64/server -ljvm Hello.cc: In function ‘int main()’: Hello.cc:22:29: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’ [-Wwrite-strings] ➜ ~ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:$JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/amd64/server ➜ ~ ./a.out Hello,World
可以通过创建一个JVM来将多个线程attach上去,相当于这个JVM启动的多个线程。这里的线程使用的是OS native thread实现。
- AttachCurrentThread
- DetachCurrentThread
8. Additional JNI Features
8.1. JNI and Threads
- MonitorEnter/MonitorExit可以操作monitor.
- 对应java里面的synchronized关键字区域 ???
8.2. Registering Native Methods
允许动态注册native methods.
8.3. Load and Unload Handlers
系统加载和卸载native library回调函数:
- JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM *jvm, void *reserved); // 返回JNI版本比如 JNI_VERSION_1_6
- JNIEXPORT void JNICALL JNI_OnUnload(JavaVM *jvm, void *reserved)
load/unload工作流程是这样的:
- The virtual machine associates each native library with the class loader L of the class C that issues the System.loadLibrary call. // 每次加载的时候创建ClassLoader,并且记录这个ClassLoader关联了哪些对象。
- The virtual machine calls the JNI_OnUnload handler and unloads the native library after it determines that the class loader L is no longer a live object. Because a class loader refers to all the classes it defines, this implies that C can be unloaded as well. // 如果ClassLoader里面没有任何live object的话,那么就会被GC
- The JNI_OnUnload handler runs in a finalizer, and is either invoked synchro-niously by java.lang.System.runFinalization or invoked asynchro-nously by the virtual machine. // unload可能会被同步调用也可能会被异步调用。
- 因此如果ClassLoader里面包含在global reference的话,那么这个class loader是不会被卸载的
9. Leveraging Existing Native Libraries
如何使用现有的native library:
- one-to-one mapping. 针对每个函数做一个包装,外部做类型转换.
- shared stubs. 做一个dispatcher函数,根据所传参数包装成为合适的C++类型,然后直接传给C++函数。但是调用C++函数这个部分需要自己实现函数调用栈。
- 个人觉得one-to-one mapping虽然实现比较麻烦,可是用起来比较简单,而shared stubs则相反。自己完全可以实现一些简单的common library来简化编写过程。
10. Traps and Pitfalls
- Error Checking
- Passing Invalid Arguments to JNI Functions
- Confusing jclass with jobject
- Truncating jboolean Arguments
- Boundaries between Java Application and Native Code
- Confusing IDs with References
- Caching Field and Method IDs
- Terminating Unicode Strings
- Violating Access Control Rules
- Disregarding Internationalization
- Retaining Virtual Machine Resources
- Excessive Local Reference Creation
- Using Invalid Local References
- Using the JNIEnv across Threads
- Mismatched Thread Models
11. Overview of the JNI Design
Locating Native Libraries
- System.loadLibrary throws an UnsatisfiedLinkError if it fails to load the named native library. 如果找不到native library就会抛出UnsatisfiedLinkError异常。
- System.loadLibrary completes silently if an earlier call to System.loadLibrary has already loaded the same native library. 如果已经加载的话就不会重复加载。
- If the underly-ing operating system does not support dynamic linking, all native methods must be prelinked with the virtual machine. 如果不支持动态链接的话就只能够预先链接做静态链接。
- ClassLoader.findLibrary 定位library路径
Linking Native Methods
- the native method by concatenating the following components:
- the prefix “Java_”
- an encoded fully qualified class name
- an underscore (“_”) separator
- an encoded method name
- for overloaded native methods, two underscores (“__”) followed by the encoded argument descriptor
- If native functions matching an encoded native method name are present in multiple native libraries, the function in the native library that is loaded first is linked with the native method. 如果存在多个定义那么使用找到的第一个使用。
- If no function matches the native method name, an UnsatisfiedLinkError is thrown. 否则抛出异常。
Passing Data
使用reference的好处可以使得访问数据更加灵活。
Accessing Objects
- Accessing Primitive Arrays
- One solution introduces a notion of “pinning” so that the native method can ask the virtual machine not to move the contents of an array. 对于原始类型数组访问的话可以考虑使用pinning的方式,这种方式直接返回数据内容而不需要copy
- The garbage collector must support pinning. In many implementations, pin-ning is undesirable because it complicates garbage collection algorithms and leads to memory fragmentation. 支持pinning首先需要GC支持,但是这样会复杂GC算法并且造成内存碎片
- The virtual machine must lay out primitive arrays contiguously in memory. Although this is the natural implementation for most primitive arrays, boolean arrays can be implemented as packed or unpacked. 其次需要VM内部实现的时候就是按照原始类型连续存放的
- GetIntArrayRegion/SetIntArrayRegion 操作的是数组的copy版本
- GetIntArrayElements/ReleaseIntArrayElements VM尽量返回pinning版本
- GetPrimitiveArrayCritical/ReleasePrimitiveArrayCritical 和上面非常类似,但是进入的是一个critical region停止GC算法,所以更有可能返回pinning版本。
- Fields and Methods
- A field or method ID remains valid until the virtual machine unloads the class or interface that defines the corresponding field or method. After the class or inter-face is unloaded, the method or field ID becomes invalid. 在class被unload之前field/method ID都是有效的。