HBase Log Splitting
http://blog.cloudera.com/blog/2012/07/hbase-log-splitting/
需要log split的原因是,在一台region server上面可能serve多个region,而这些region的WAL都记录在同一个文件里面。如果一个region server挂掉的话,那么对应的region需要放在其他region server上面进行serve,而在serve之前需要做日志恢复,这个日志包括所有对于这个region的修改,所以这就牵扯到了log split。所以所谓的log split是将一个WAL文件,按照不同region拆分成为多个文件,每个文件里面只是包含一个region的内容。log split发生在启动一个region server之前。
Log splitting is done by HMaster as the cluster starts or by ServerShutdownHandler as a region server shuts down. Since we need to guarantee consistency, affected regions are unavailable until data is restored. So we need to recover and replay all WAL edits before letting those regions become available again. As a result, regions affected by log splitting are unavailable until the process completes and any required edits are applied.(log split过程是由master来完成的,为了保证一致性在进行split期间受影响的region不能够服务,下面是一个log splitting的图示流程:
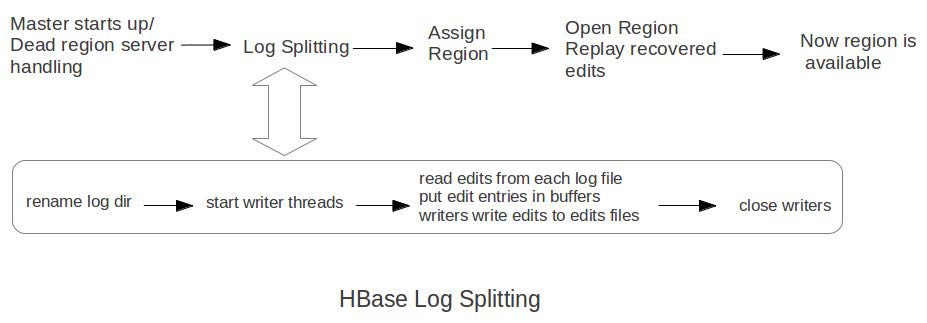
- rename log dir是将对应的region server的目录重命名,这样是为了确保不会出现如果master认为region server挂掉但是实际上region server还在serve的情况。重命名为 hbase.logs/<host>, <port>,<startcode>-splitting
- It is important that HBase renames the folder. A region server may still be up when the master thinks it is down. The region server may not respond immediately and consequently doesn’t heartbeat its ZooKeeper session. HMaster may interpret this as an indication that the region server has failed. If the folder is renamed, any existing, valid WAL files still being used by an active but busy region server are not accidentally written to.
- hbase.logs/srv.example.com,60020,1254173957298-splitting
- start write threads 启动多个线程来写(如果存在多个文件的话也可以使用多个线程来读取),但是事实上这样效率依然不高,因为存在很多机器空闲。
- read edits from each log file, put edit entries in buffers, writers write edits to edits files. 读线程来进行拆分,将需要write的内容丢给写线程完成。
- 每个线程写入的文件为/hbase/<table_name>/<region_id>/recovered.edits/.temp
- 一旦写成功之后就会重命名为/hbase/<table_name>/<region_id>/recovered.edits/<sequenceid>,其中sequenceid是最后一条写入这个file的log对应的unique operation id.
- As a result, when replaying the recovered edits, it is possible to determine if all edits have been written. If the last edit that was written to the HFile is greater than or equal to the edit sequence id included in the file name, it is clear that all writes from the edit file have been completed.(这样一旦在做文件恢复的时候就可以很容易地确定这个恢复文件是否需要读取。如果在HFile里面最大的sequence id比这个文件名显示的seq id大的话,那么可以认为不需要replay这个文件)
- close writers 关闭写线程以及对应的HDFS文件
- 指定新的region server来serve某些region,并且读取这个region对应的HDFS看是否有恢复文件,如果存在恢复文件的话那么就需要进行replay.
Times to complete single threaded log splitting vary, but the process may take several hours if multiple region servers have crashed. Distributed log splitting was added in HBase version 0.92 (HBASE-1364) by Prakash Khemani from Facebook. It reduces the time to complete the process dramatically, and hence improves the availability of regions and tables. For example, we knew a cluster crashed. With single threaded log splitting, it took around 9 hours to recover. With distributed log splitting, it just took around 6 minutes.(由单个master来完成log splitting的工作非常耗时,所以引入了distributed log splitting这个机制,由facebook的工程师实现的)
distributed log splitting 机制非常简单,就是将所有需要被splitting的WAL分布式并行地来完成。首先将这些文件全部放在zookeeper上面,然后cluster里面的机器可以上去认领自己来进行split那个日志,当然也要考虑这个机器在split日志的时候自己挂掉的情况。
- With distributed log splitting, the master is the boss. It has a split log manager to manage all log files which should be scanned and split. Split log manager puts all the files under the splitlog ZooKeeper node (hbase/splitlog) as tasks. For example, while in zkcli, “ls /hbase/splitlog” returns: [hdfs://host2.sample.com:56020/hbase.logs/host8.sample.com,57020,1340474893275-splitting/host8.sample.com%3A57020.1340474893900, hdfs://host2.sample.com:56020/hbase/.logs/host3.sample.com,57020,1340474893299-splitting/host3.sample.com%3A57020.1340474893931, hdfs://host2.sample.com:56020/hbase/.logs/host4.sample.com,57020,1340474893287-splitting/host4.sample.com%3A57020.1340474893946] (master在zookeeper节点/hbase/splitlog下面增加需要做split的文件,而master本身只需要监控这个节点下面是否还有剩余的文件)
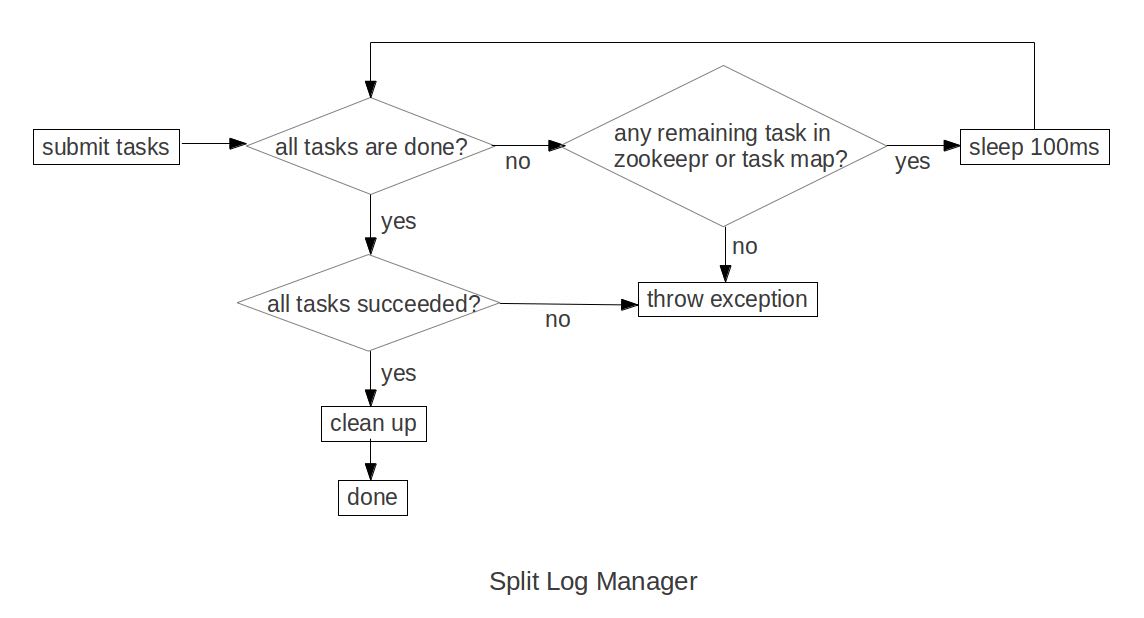
- In each region server, there is a daemon thread called split log worker. Split log worker does the actual work to split the logs. The worker watches the splitlog znode all the time. If there are new tasks, split log worker retrieves the task paths, and then loops through them all to grab any one which is not claimed by other worker yet. After it grabs one, it tries to claim the ownership of the task, to work on the task if successfully owned, and to update the task’s state properly based on the splitting outcome. After the split worker completes the current task, it tries to grab another task to work on if any remains.(如果得到了这个log split的权限的话,那么就修改这个task的ownership)
这个功能通过参数 hbase.master.distributed.log.splitting = true 来进行设置,split log manager也启动一个monitor thread来监控zookeeper节点观察出现的问题,逻辑如下:
- Checks if there are any dead split log workers queued up. If so, it will resubmit those tasks owned by the dead workers. If the resubmit fails due to some ZooKeeper exception, the dead worker is queued up again for retry.
- Checks if there are any unassigned tasks. If so, create an ephemeral rescan node so that each split log worker is notified to re-scan unassigned tasks via the nodeChildrenChanged ZooKeeper event.(如果存在一些unassigned task的话,那么创建一个临时节点来触发worker得到事件,这样worker就会重新扫描看是否存在没有完成的task)
- Checks those assigned tasks if they are expired. If so, move the task to TASK_UNASSIGNED state again so that they can be retried. These tasks could be assigned to some slow workers, or could be already finished. It is fine since the split can be retried due to the idempotency of the log splitting task; that is, the same log splitting task can be processed many times without causing any problem.(如果task过期的话,可能是因为分配到slow worker或者是已经计算完毕,那么就会被重新设置TASK_UNASSIGNED.但是这个对于正确性没有影响因为是幂等的)