装配SSD
@2015-05-04
大约在半年之前把,台式机的HDD就被SMART检查出有问题了,但是考虑到更换系统挺麻烦的,就一直拖着。直到最近觉得不太能忍受了,开机需要60s以上,打开浏览器什么的都需要等一段时间,最不能忍受的是编辑文件保存一下就需要等1-2s. 然后看了一下自己硬盘空间,虽然是1TB但是实际只使用了<50G,所以买个250G的SSD应该是足够了。
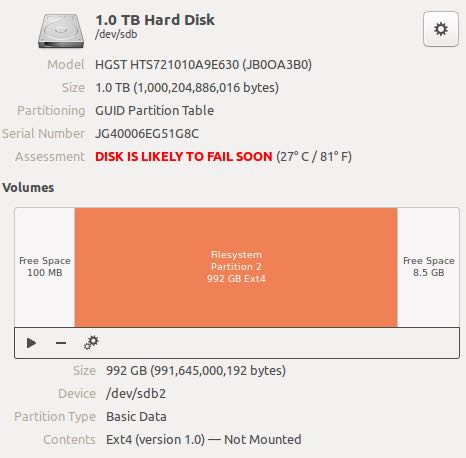
想到了就买,也没有在太多品牌和价格上纠结,就从 京东 上买了这款:三星(SAMSUNG)850 EVO系列 250G 2.5英寸 SATA-3固态硬盘(MZ-75E250B/CN). 安装好系统之后,继续挂着原来的HDD,这样可以把原来硬盘上的文件copy过来。从安装到配置好,大约花了2个小时左右,主要还是SSD的读写速度快。现在启动时间大约在10s以内,打开浏览器2-3s左右,感觉好极了。
之前看过SSD的 科普文章 说TRIM指令可以让SSD利用率更高,所以最好确认自己的SSD支持TRIM指令。下面命令用来确认支持TRIM,grep "Data Set Management TRIM supported (limit 8 blocks)"
➜ ~ sudo hdparm -I /dev/sda
[sudo] password for dirlt:
/dev/sda:
ATA device, with non-removable media
Model Number: Samsung SSD 850 EVO 250GB
Serial Number: S22SNXAG302833K
Firmware Revision: EMT01B6Q
Transport: Serial, ATA8-AST, SATA 1.0a, SATA II Extensions, SATA Rev 2.5, SATA Rev 2.6, SATA Rev 3.0
Standards:
Used: unknown (minor revision code 0x0039)
Supported: 9 8 7 6 5
Likely used: 9
Configuration:
Logical max current
cylinders 16383 16383
heads 16 16
sectors/track 63 63
--
CHS current addressable sectors: 16514064
LBA user addressable sectors: 268435455
LBA48 user addressable sectors: 488397168
Logical Sector size: 512 bytes
Physical Sector size: 512 bytes
Logical Sector-0 offset: 0 bytes
device size with M = 1024*1024: 238475 MBytes
device size with M = 1000*1000: 250059 MBytes (250 GB)
cache/buffer size = unknown
Nominal Media Rotation Rate: Solid State Device
Capabilities:
LBA, IORDY(can be disabled)
Queue depth: 32
Standby timer values: spec'd by Standard, no device specific minimum
R/W multiple sector transfer: Max = 1 Current = 1
DMA: mdma0 mdma1 mdma2 udma0 udma1 udma2 udma3 udma4 udma5 *udma6
Cycle time: min=120ns recommended=120ns
PIO: pio0 pio1 pio2 pio3 pio4
Cycle time: no flow control=120ns IORDY flow control=120ns
Commands/features:
Enabled Supported:
* SMART feature set
Security Mode feature set
* Power Management feature set
* Write cache
* Look-ahead
* Host Protected Area feature set
* WRITE_BUFFER command
* READ_BUFFER command
* NOP cmd
* DOWNLOAD_MICROCODE
SET_MAX security extension
* 48-bit Address feature set
* Device Configuration Overlay feature set
* Mandatory FLUSH_CACHE
* FLUSH_CACHE_EXT
* SMART error logging
* SMART self-test
* General Purpose Logging feature set
* WRITE_{DMA|MULTIPLE}_FUA_EXT
* 64-bit World wide name
Write-Read-Verify feature set
* WRITE_UNCORRECTABLE_EXT command
* {READ,WRITE}_DMA_EXT_GPL commands
* Segmented DOWNLOAD_MICROCODE
* Gen1 signaling speed (1.5Gb/s)
* Gen2 signaling speed (3.0Gb/s)
* Gen3 signaling speed (6.0Gb/s)
* Native Command Queueing (NCQ)
* Phy event counters
* READ_LOG_DMA_EXT equivalent to READ_LOG_EXT
DMA Setup Auto-Activate optimization
Device-initiated interface power management
* Asynchronous notification (eg. media change)
* Software settings preservation
Device Sleep (DEVSLP)
* SMART Command Transport (SCT) feature set
* SCT Write Same (AC2)
* SCT Error Recovery Control (AC3)
* SCT Features Control (AC4)
* SCT Data Tables (AC5)
* reserved 69[4]
* DOWNLOAD MICROCODE DMA command
* SET MAX SETPASSWORD/UNLOCK DMA commands
* WRITE BUFFER DMA command
* READ BUFFER DMA command
* Data Set Management TRIM supported (limit 8 blocks)
Security:
Master password revision code = 65534
supported
not enabled
not locked
frozen
not expired: security count
supported: enhanced erase
2min for SECURITY ERASE UNIT. 8min for ENHANCED SECURITY ERASE UNIT.
Logical Unit WWN Device Identifier: 5002538d4002292f
NAA : 5
IEEE OUI : 002538
Unique ID : d4002292f
Checksum: correct
Device Sleep:
DEVSLP Exit Timeout (DETO): 50 ms (drive)
Minimum DEVSLP Assertion Time (MDAT): 30 ms (drive)
为了利用好这块SSD,我还在网上查了一下推荐设置,总结如下:(一些意见我没有采纳)
- http://www.leaseweblabs.com/2013/07/5-crucial-optimizations-for-ssd-usage-in-ubuntu-linux/
- http://www.howtogeek.com/176978/ubuntu-doesnt-trim-ssds-by-default-why-not-and-how-to-enable-it-yourself/
- https://sites.google.com/site/easylinuxtipsproject/ssd
- SATA设备使用AHCI模式 # BIOS settings, Integrated Peripherals, SATA Configuration
- 减少swap操作 # echo -e "vm.swappiness=0" | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf
- 禁止记录atime # 编辑/etc/fstab, 修改"errors=remount-ro"为"noatime,errors=remount-ro",然后重启
- 使用fstrim功能 # Ubuntu14.04默认有/etc/cron.weekly/fstrim每周执行trim,用来删除系统无用块
- 不使用SSD trim操作 # 虽然Linux也支持SSD trim(real-time trim), 但是会造成性能下降
- 可以考虑把fstrim功能添加到每次启动(/etc/rc.local)
- 可以考虑空出7%磁盘作为overprovisioning.
高版本Linux内核已经支持自动对齐,但是似乎使用自带disk工具不能对新分区对齐。推荐使用GParted这个工具来做分区,它可以自动完成新分区的对齐。
- http://tytso.livejournal.com/2009/02/20/
- http://www.linux-mag.com/id/8397/
- https://wiki.mageia.org/en/Installation_on_a_SSD_(Solid_State_Drive)
➜ ~ sudo fdisk -lu /dev/sda [sudo] password for dirlt: Disk /dev/sda: 250.1 GB, 250059350016 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 30401 cylinders, total 488397168 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x00043176 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sda1 * 2048 195311615 97654784 83 Linux /dev/sda2 195313662 459102338 131894338+ f W95 Ext'd (LBA) /dev/sda5 195315712 390627327 97655808 83 Linux /dev/sda6 400414720 459102207 29343744 83 Linux /dev/sda7 390629376 400412671 4891648 82 Linux swap / Solaris
确保除了LBA之外的devices start都是2048的倍数 (start的单位是sector? 2048 * 512 bytes = 1MB)
另外关于SSD寿命问题可以看看这个帖子 http://zhidao.baidu.com/question/220559125.html
SSD完全不用担心寿命问题,SSD和机械硬盘的原理不一样,机械硬盘比如你系统装在C盘,C盘在磁盘的最外圈,所有它会一直在最外圈读和写。SSD的主控会让SSD平均写入,就是永远优先写在使用次数少的存储空间上,就是说就算你拿一个文件反复在SSD上复制删除,其实他每次写入的空间是不一样的,所以SSD的理论上更确切的应该说SSD可以写入容量X1万。拿主流64G的算,理论上就是60GX10000=60万G,实际应用算它打对折30万G。每天写入200G的话可以用4年多,但是能用200G吗?所有不用担心寿命问题,SSD的换掉肯定是被淘汰或坏掉的,绝对不会是写完的。SSD好坏很难说,基本用价格和品牌衡量吧,现在价格64G的在800以上的为好,再低就有问题了。因特尔,美光,海盗船,芝奇,金士顿什么的都可以。