Computer Architecture Readings - Princeton - Review/Superscalar/VLIW
ELE/COS 475 Computer Architecture
计算机架构在不断变化,有同时来自门电路技术改进以及软件需求。计算机体系结构主要研究中间三层:ISA,微架构,RTL。下面开始的门电路/逻辑电路属于更底层的硬件层,而上面则属于软件层。
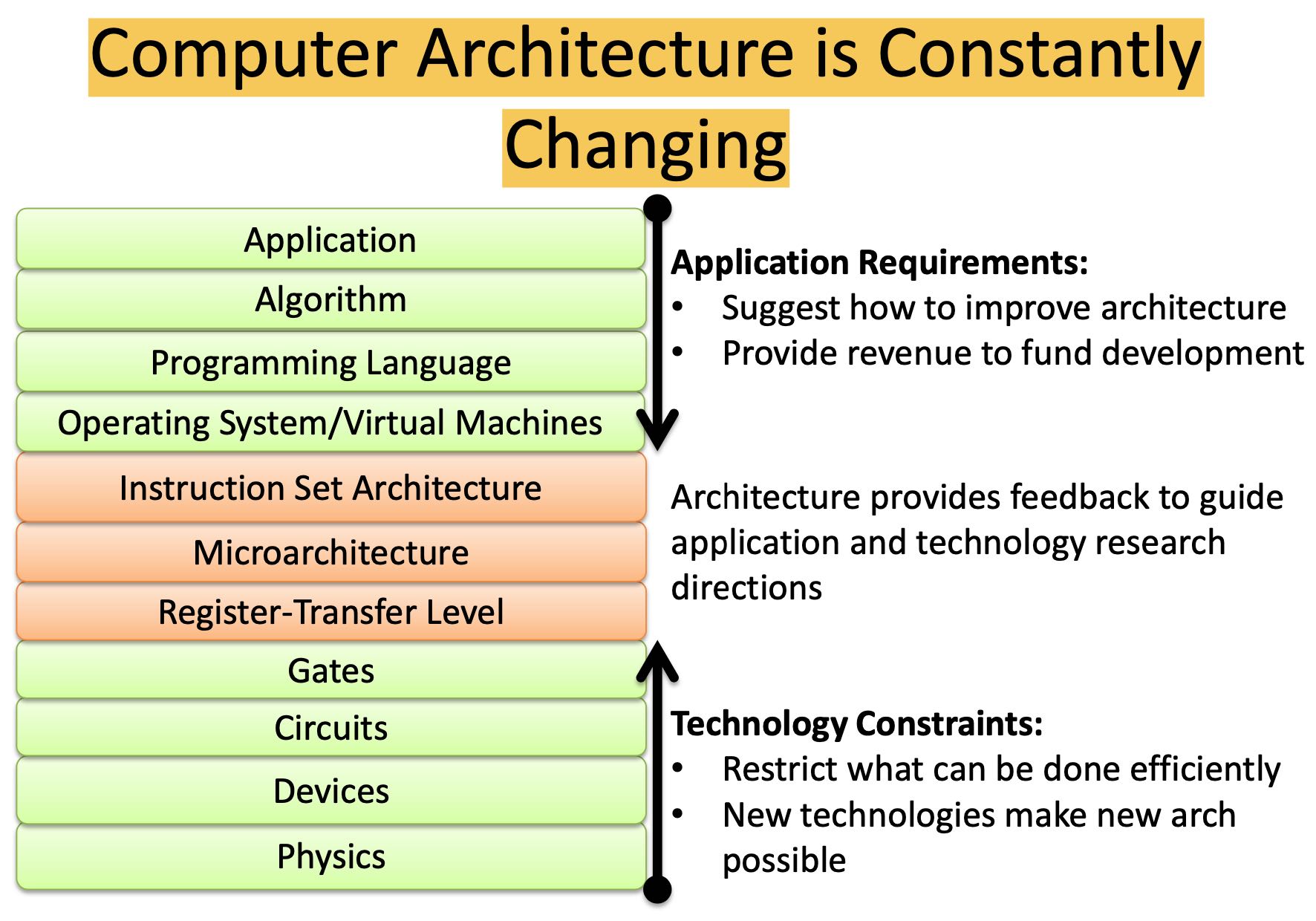
ISA和Microarch之间的差别,对于软件开发者只需要关注到ISA这层就行,而MA层则是由芯片设计者来决定如何高效地实现ISA这层语义。
Architecture vs. Microarchitecture “Architecture”/Instruction Set Architecture:
- Programmer visible state (Memory & Register)
- Operations (Instructions and how they work)
- Execution Semantics (interrupts)
- Input/Output
- Data Types/Sizes
Microarchitecture/Organization:
- Tradeoffs on how to implement ISA for some metric (Speed, Energy, Cost)
- Examples: Pipeline depth, number of pipelines, cache size, silicon area, peak power, execution ordering, bus widths, ALU widths
ISA差异很大的原因有下面这些
Technology Influenced ISA
- Storage is expensive, tight encoding important
- Reduced Instruction Set Computer
- Remove instructions until whole computer fits on die
- Multicore/Manycore – Transistors not turning into sequential performance
Application Influenced ISA
- Instructions for Applications
- DSP instructions
- Compiler Technology has improved
- SPARC Register Windows no longer needed – Compiler can register allocate effectively
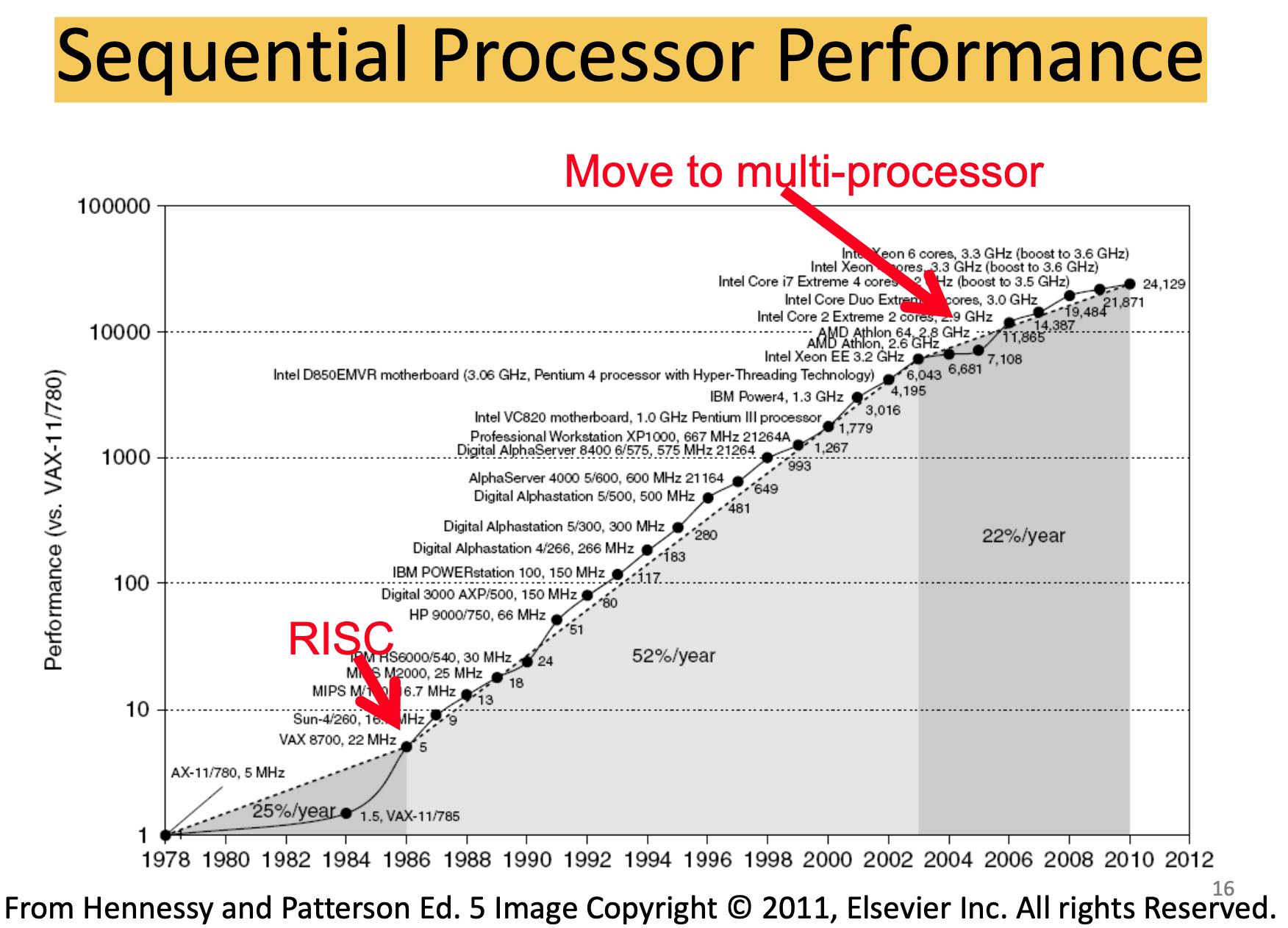
顺序处理器的性能变化,RISC出现在1986年,2006年开始放弃在单核上做改进转向多核。
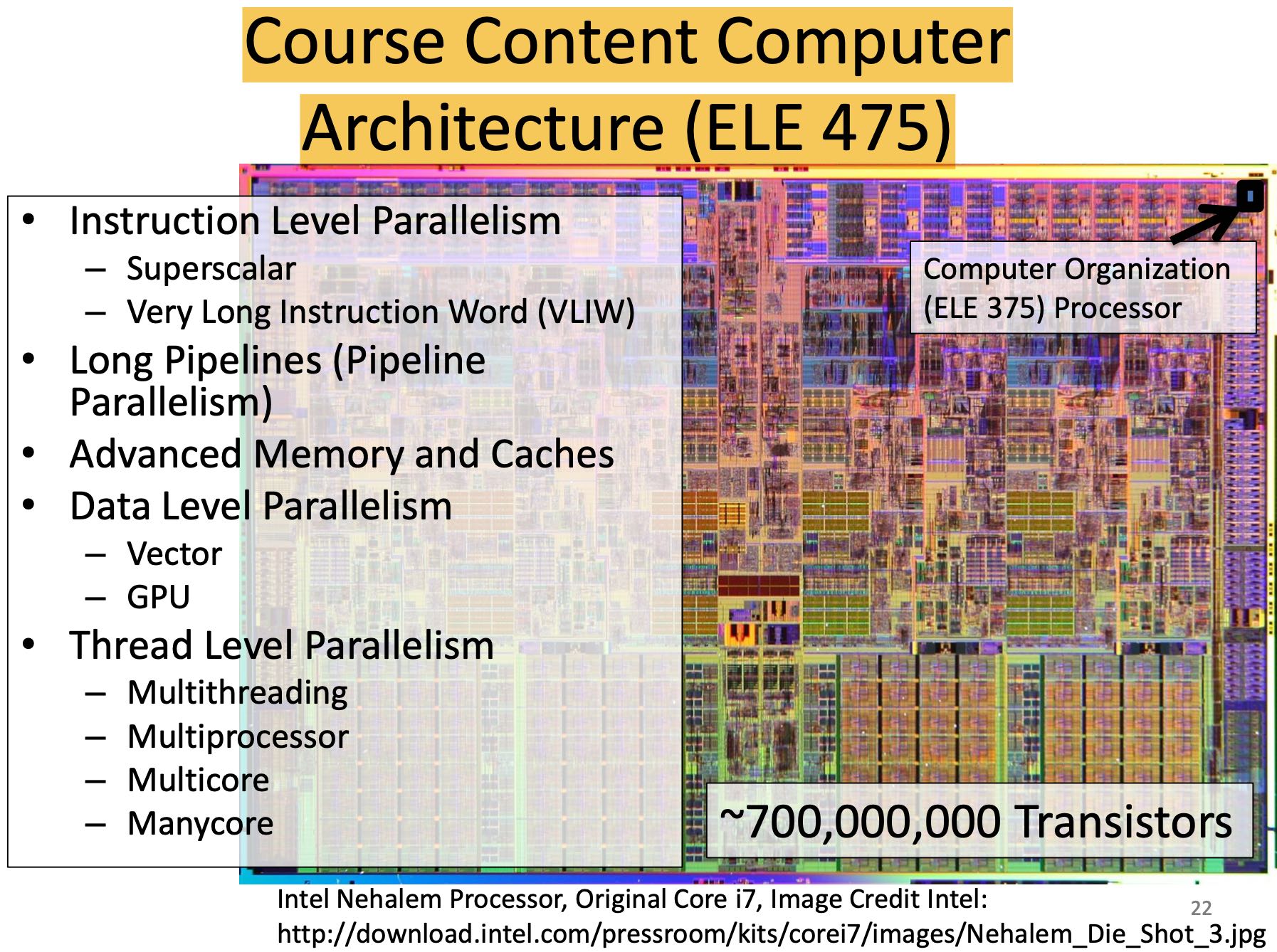
现代处理器需要考虑的事情非常多:指令/数据/线程级别并行,超长流水,内存和缓存技术
指令中几种阻碍深流水线的因素:
- Structural Hazard: An instruction in the pipeline needs a resource being used by another instruction in the pipeline (使用到相同的运算/控制单元,解决办法如下)
- Schedule: Programmer explicitly avoids scheduling instructions that would create structural hazards 调整指令熟顺序
- Stall: Hardware includes control logic that stalls until earlier instruction is no longer using contended resource 暂停流水
- Duplicate: Add more hardware to design so that each instruction can access independent resources at the same time 冗余的运算/控制单元
- Data Hazard: An instruction depends on a data value produced by an earlier instruction(多条指令之间存在数据依赖,解决办法如下)
- Schedule: Programmer explicitly avoids scheduling instructions that would create data hazards 调整指令顺序
- Stall: Hardware includes control logic that freezes earlier stages until preceding instruction has finished producing data value 暂停流水
- Bypass: Hardware datapath allows values to be sent to an earlier stage before preceding instruction has left the pipeline 调整流水线结构,可以提前得到数据
- Speculate: Guess that there is not a problem, if incorrect kill speculative instruction and restart 推测执行
- Control Hazard: Whether or not an instruction should be executed depends on a control decision made by an earlier instruction(控制结构比jb/jbe/jmp这些,使用分支预测解决)
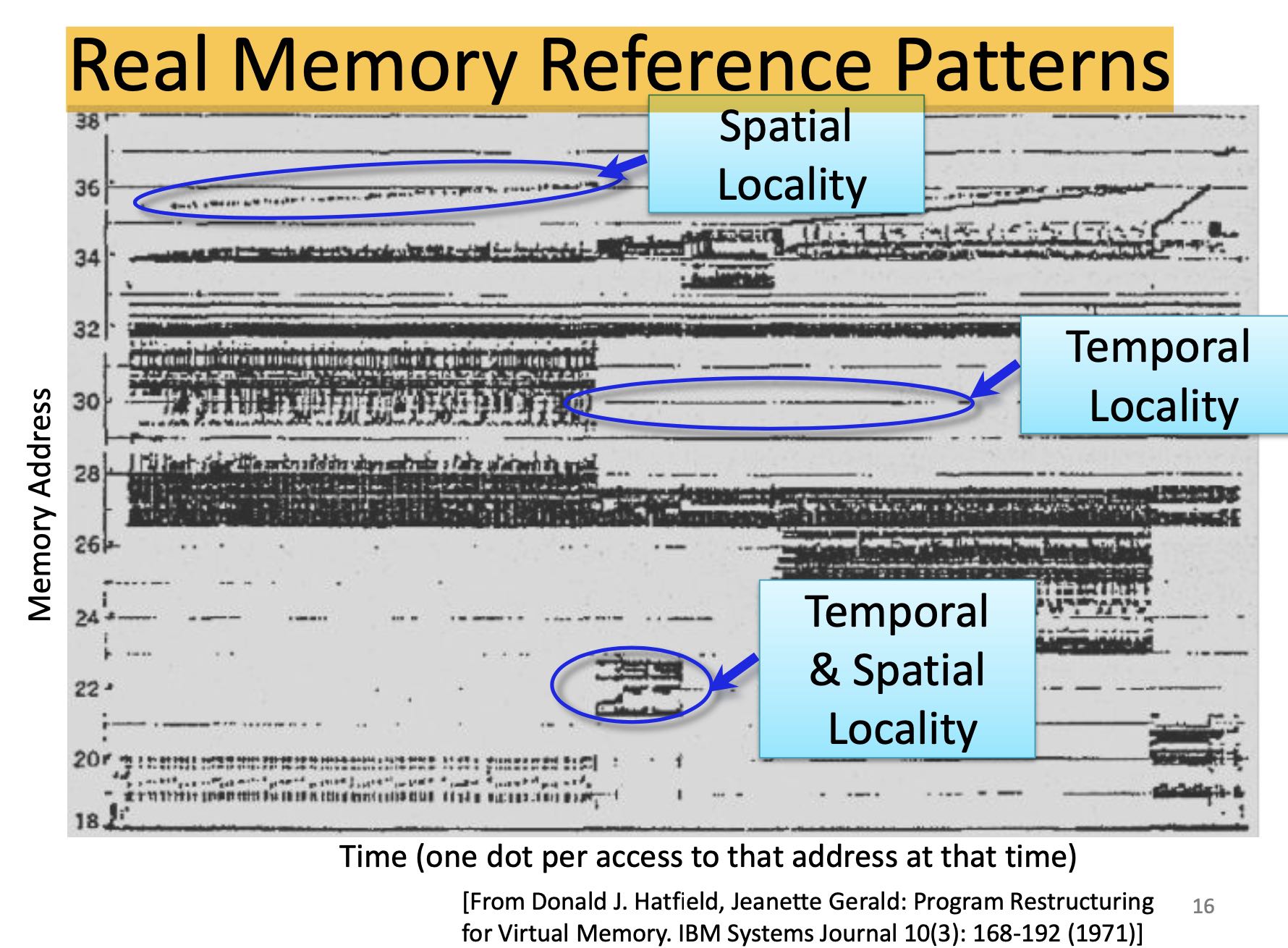
几种常见/可预测的内存访问模式,可以看到都是满足时间/空间局部性的:获取指令,堆栈访问,向量/标量化数据的访问。
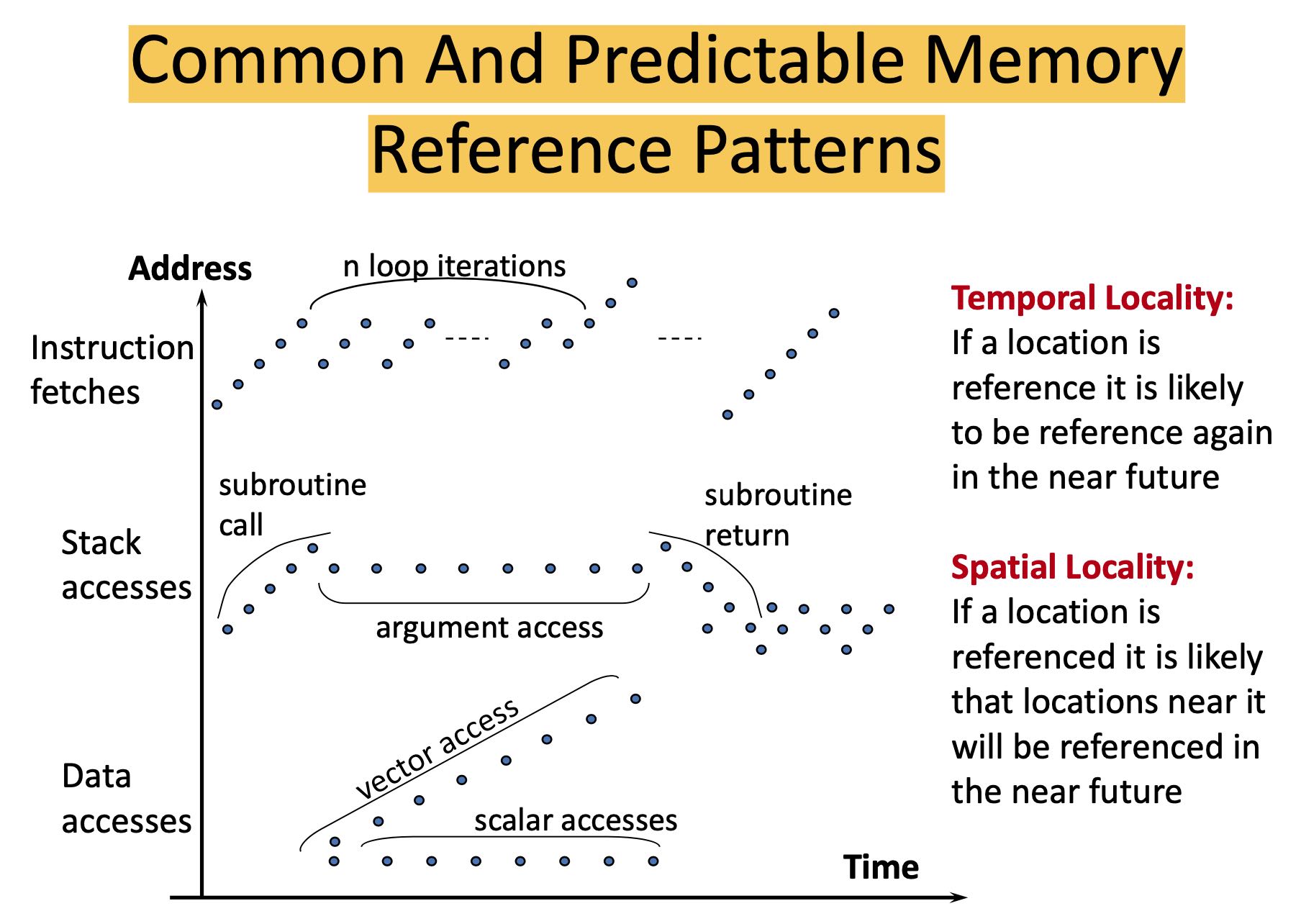
可视化地观察时间/空间局部性
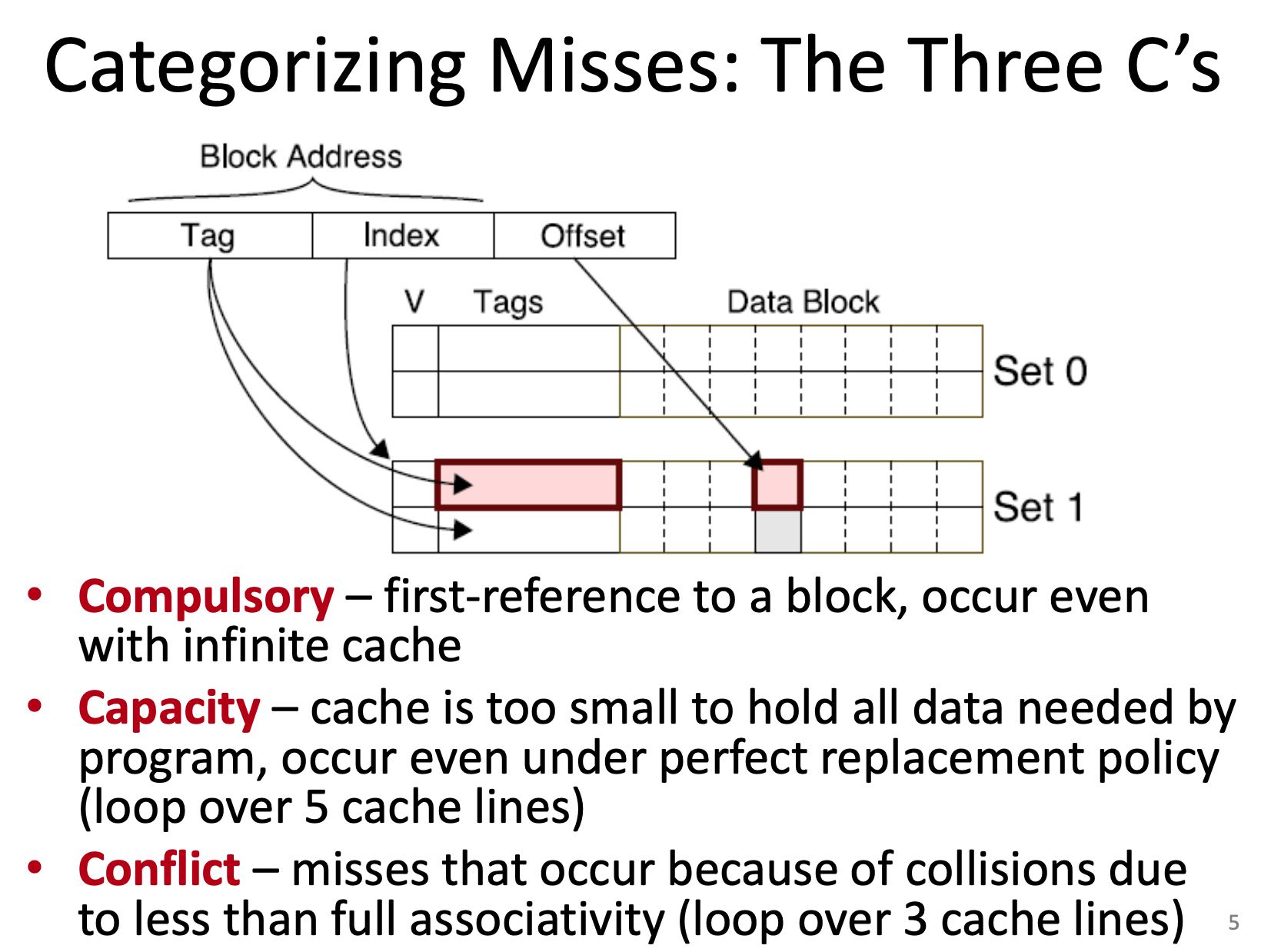
Cache几种Missing分类:3C, Compulsory(第一次访问), Capacity(容量不够造成的淘汰), Conflict(冲突造成的淘汰, 实际上容量是足够的)
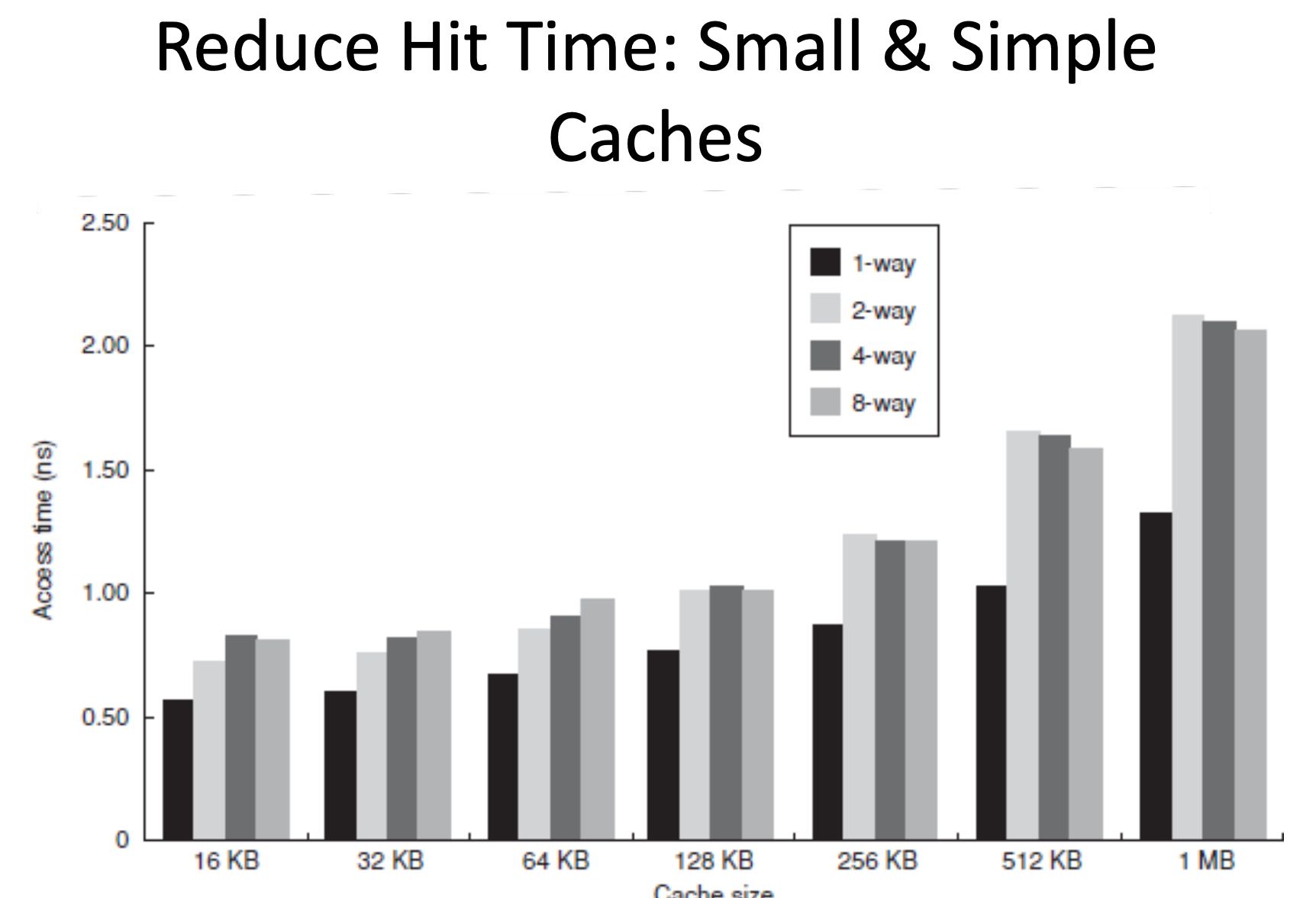
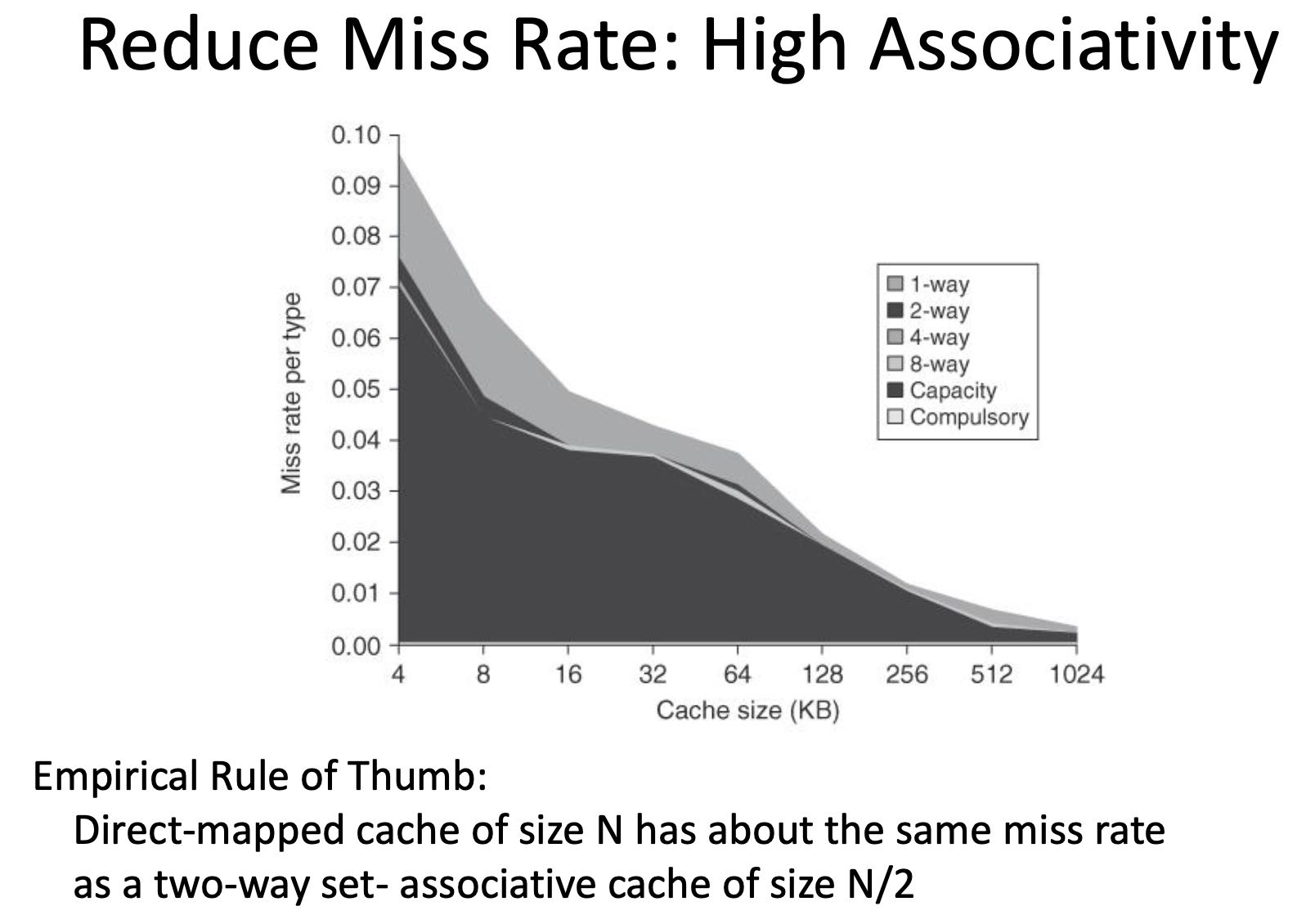
Cache设计上的权衡:N-way, Block Cache, Cache Size. Block Cache在64, N-way上越大越好,Cache Size越大越好。
N-way上, 1-way的访问时间是最短的,但是2/4/8时间其实差别不大很大,但是1-way的miss rate却非常高,所以理论上选择8-way是应该是更好的选择。
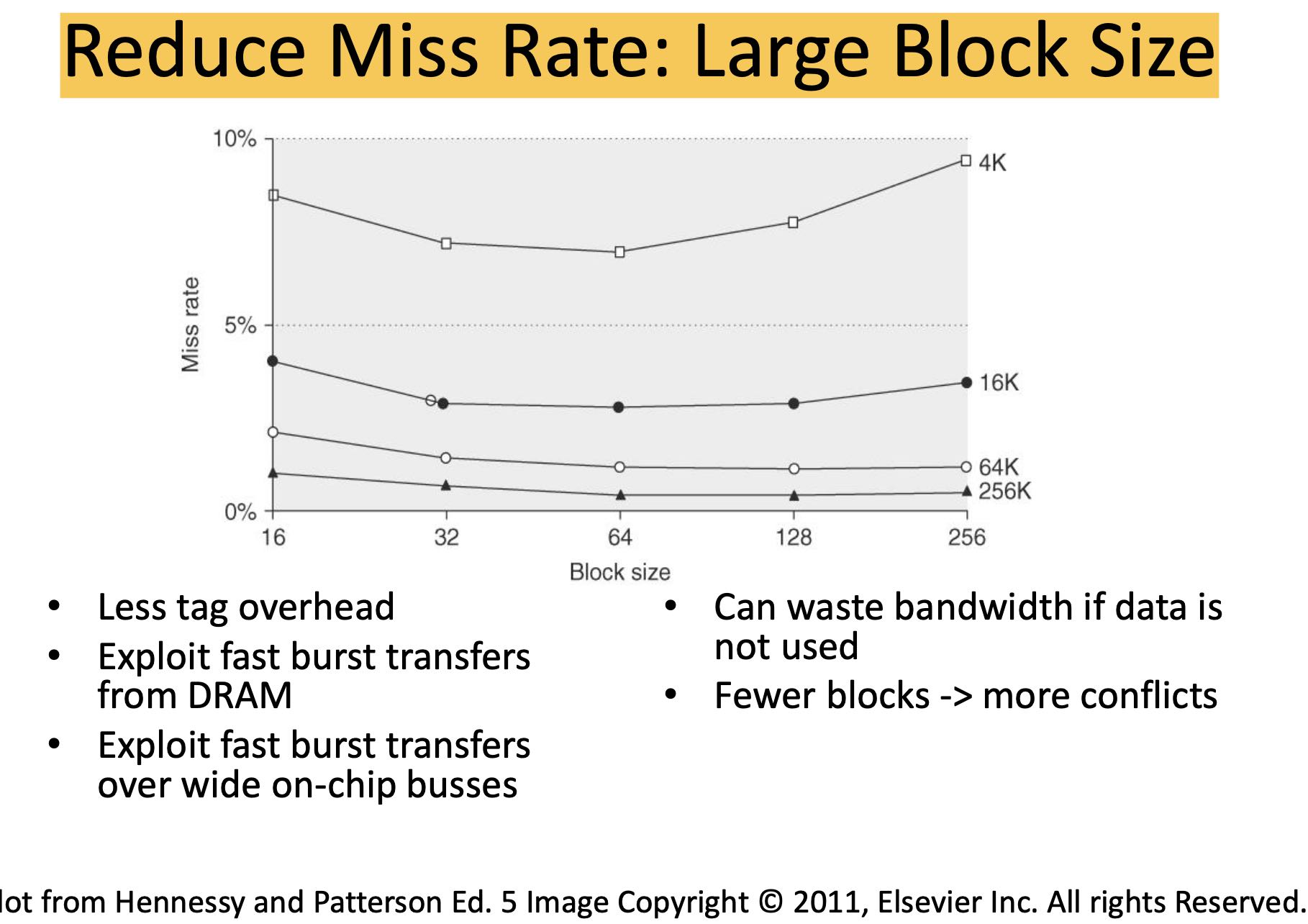
Cache Block Size Pros & Cons: 好处就是一次获取数据更多带宽更大,而坏处就是如果数据没有完全访问的话那么就相当于浪费带宽,而且更大的Block Size会导致更少的cache items, 冲突率更大。从下图可以看到几乎Block Size = 64 是个最优值,不过也不好说是不是软件在优化上就使用了block size = 64这个事实。
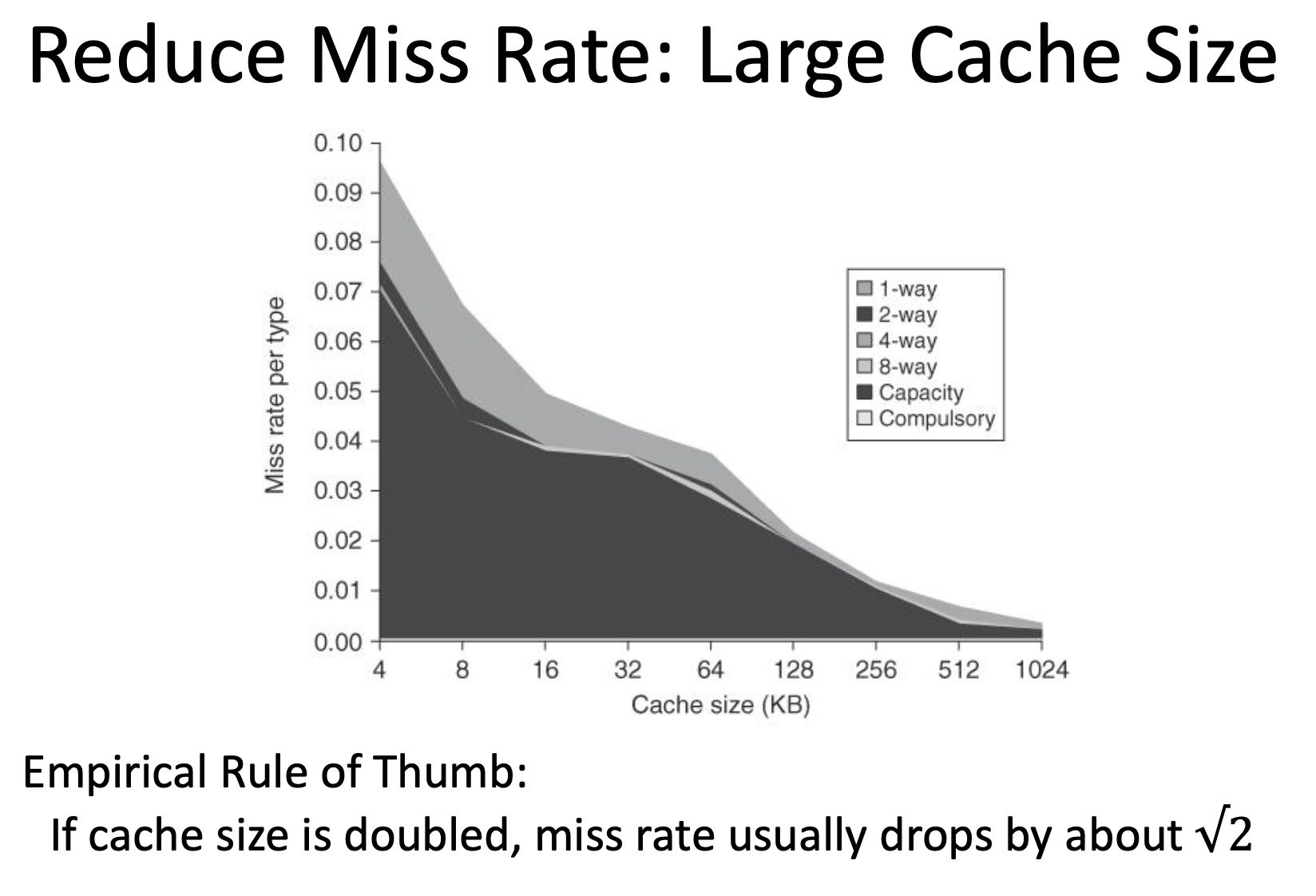
Cache Size有个法则就是:Cache Size翻倍, miss rate降低30%. (1-1/(2^0.5))
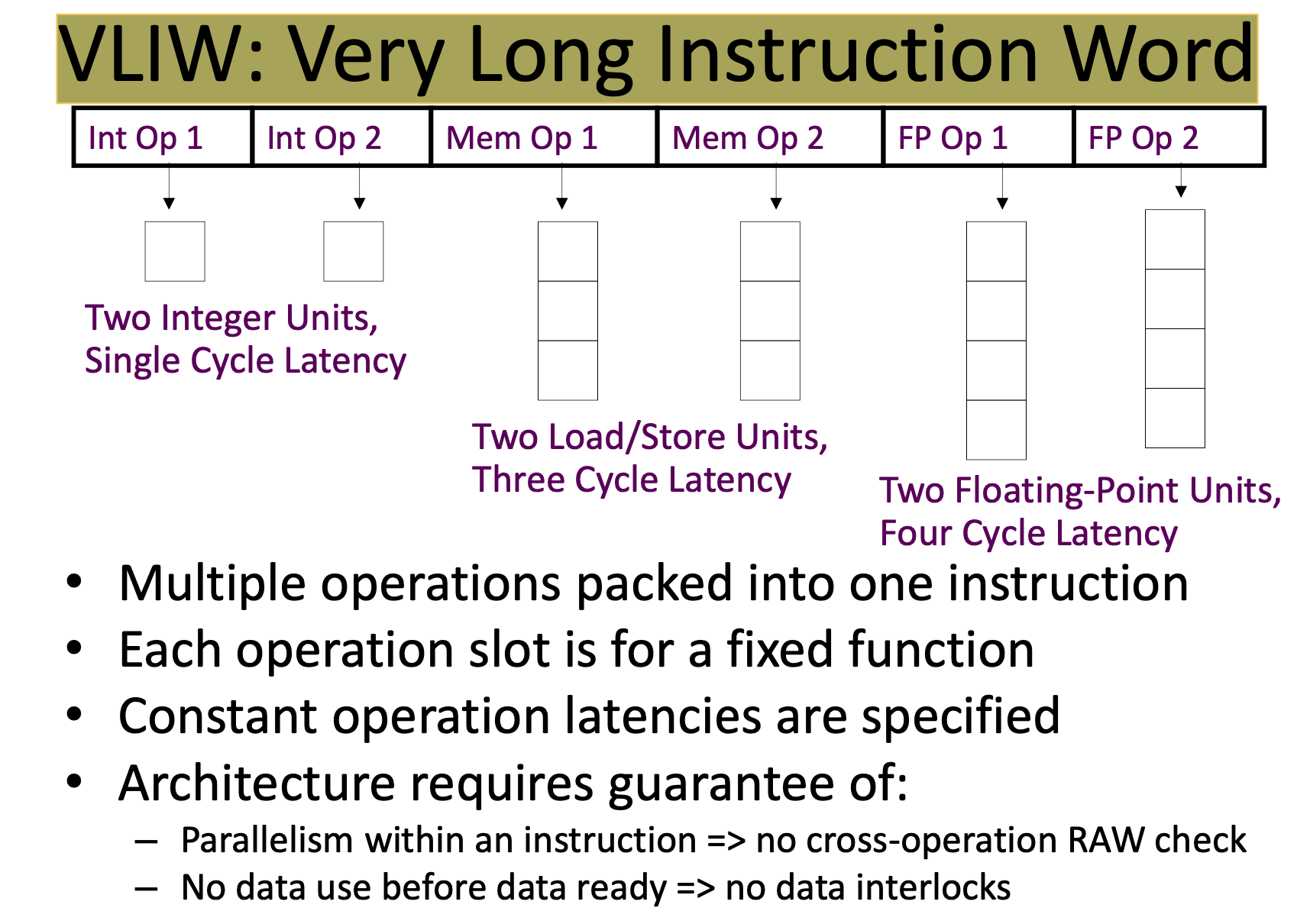
VLIW要求将多条操作打包在一个指令里面,并且操作之间是相互独立的:使用不同的计算/控制单元,不存在数据之间的依赖。从PPT里面来看,每个slot里面还有具体的cycle latency要求,看起来这个对于编译器的要求非常高。
实际上VLIW问题是比较多的(一些点没有看懂):
VLIW Compiler Responsibilities
- Schedule operations to maximize parallel execution
- Guarantees intra-instruction parallelism
- Schedule to avoid data hazards (no interlocks)
- Typically separates operations with explicit NOPs
Problems with “Classic” VLIW
- Object-code compatibility (二进制兼容性)
- have to recompile all code for every machine, even for two machines in same generation
- Object code size (二进制大小)
- instruction padding wastes instruction memory/cache
- loop unrolling/software pipelining replicates code
- Scheduling variable latency memory operations
- caches and/or memory bank conflicts impose statically unpredictable variability
- Knowing branch probabilities
- Profiling requires an significant extra step in build process
- Scheduling for statically unpredictable branches
- optimal schedule varies with branch path
- Precise Interrupts can be challenging – Does fault in one portion of bundle fault whole bundle? – EQ Model has problem with single step, etc.