Binary Indexed Tree(Fenwick Tree)
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/binary-indexed-tree-or-fenwick-tree-2/
首先需要了解负数的二进制表示:负数的二进制表示是取反然后+1
def binstr(x):
ss = []
for i in range(32):
ss.append((x >> i) & 0x1)
ss = ss[::-1]
return ''.join(map(str, ss))
for x in range(10, 16, 2):
print('bin({:>4s}) = {}'.format(str(x), binstr(x)))
y = -x
print('bin({:>4s}) = {}'.format(str(y), binstr(y)))
bin( 10) = 00000000000000000000000000001010
bin( -10) = 11111111111111111111111111110110
bin( 12) = 00000000000000000000000000001100
bin( -12) = 11111111111111111111111111110100
bin( 14) = 00000000000000000000000000001110
bin( -14) = 11111111111111111111111111110010
然后了解一下index & (-index) 这个操作的含义:找到lsb(找到最低位置的1)
print(12 & (-12)) print(binstr(12)) 4 00000000000000000000000000001100
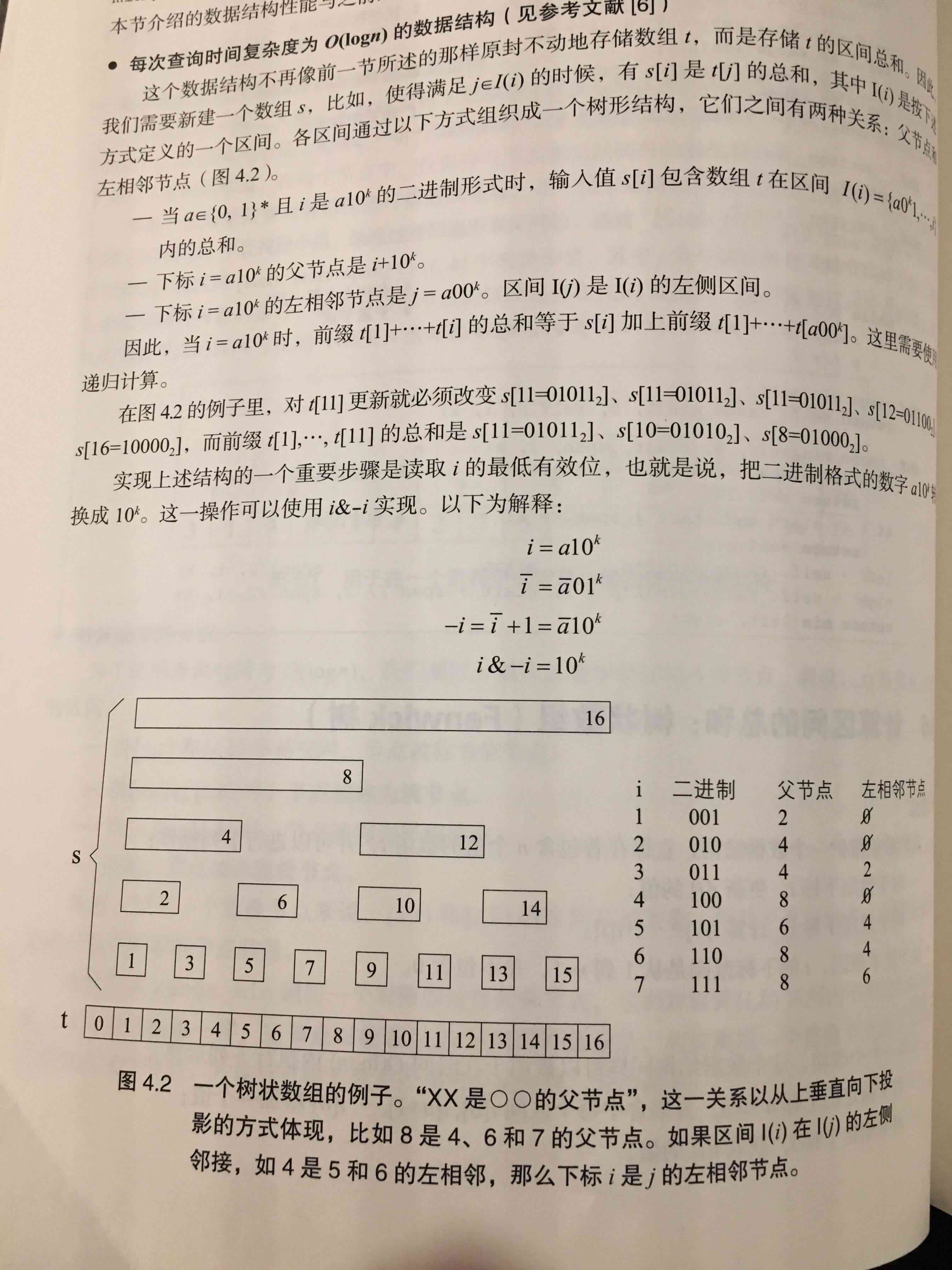
最下面图里面给出的 i & -i 的操作解释很好:
- 假设i = a 1 0k 的话
- ~i = (~a) 0 1k
- -i = (~a) 1 0k
- i & -i = 1 0 0k
UPDATE@201809: 最下面的配图可能有助于理解这棵树的组织
Binary Indexed Tree实际上进行分段存储,每段长度都是2 ** k - 1,每段里面可以继续拆分:
以31为例:31 = 16 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1. 那么可以分为五段:
1. B[16] = nums[1] + … nums[16] 2. B[24] = nums[17] + … nums[24] 3. B[28] = nums[25] + … nums[28] 4. B[30] = nums[29] + nums[30] 5. B[31] = nums[31]
这个过程就是不断地 index -= (index & -index).
然后考虑一下对于nums[index]可能会影响到哪些B呢?假设len(nums) == 32, index = 29. 从上面例子看到
1. B[30] = nums[29] + nums[30] 2. B[32] = nums[1] + … nums[32]
所以这个过程和上面相反,index += (index & -index).
/* n --> No. of elements present in input array. BITree[0..n] --> Array that represents Binary Indexed Tree. arr[0..n-1] --> Input array for whic prefix sum is evaluated. */ // Returns sum of arr[0..index]. This function assumes // that the array is preprocessed and partial sums of // array elements are stored in BITree[]. int getSum(int BITree[], int index) { int sum = 0; // Iniialize result // index in BITree[] is 1 more than the index in arr[] index = index + 1; // Traverse ancestors of BITree[index] while (index>0) { // Add current element of BITree to sum sum += BITree[index]; // Move index to parent node in getSum View index -= index & (-index); } return sum; } // Updates a node in Binary Index Tree (BITree) at given index // in BITree. The given value 'val' is added to BITree[i] and // all of its ancestors in tree. void updateBIT(int BITree[], int n, int index, int val) { // index in BITree[] is 1 more than the index in arr[] index = index + 1; // Traverse all ancestors and add 'val' while (index <= n) { // Add 'val' to current node of BI Tree BITree[index] += val; // Update index to that of parent in update View index += index & (-index); } }