An Incremental Approach to Compiler Construction (Abdulaziz Ghuloum)
这是一篇公开论文,可以在google上面搜索到。这篇论文主要探讨如何使用增量开发方式来构建编译器。
传统开发方式认为编译器是一个大的整体,先要清楚地定义好词法,文法,语义以及类型,然后从词法分析器, 语法分析器,类型检查和语义检查器,代码生成器,优化器这样的顺序来逐个实现模块,最后把整个模块串联起来。 所以许多编译器教材也是按照这个顺序组织内容的,最后可能会花很小的一篇章节说如何将每个模块串联起来。
这种教学方式和开发方式会让学生只见树木不见森林,缺乏对编译器有一个完整的认识,当然也会提高编写编译器的难度。 作者在这篇论文中提倡,我们应该先把整个流程跑通比如输入一段简单代码就可以生成对应的汇编代码,然后不断地往上面增加功能, 增加语法和语义以及对应的汇编代码,最后得到一个不断在完善中的编译器。
我在wiki上看到了作者也是 Ikarus(scheme编译器)的作者 Ikarus (Scheme implementation) - Wikipedia. 导师是大名鼎鼎的 R. Kent Dybvig - Wikipedia. 我对Dybvig的所有了解都是来自于王垠的文章 Chez Scheme 的传说
这篇论文有一个更加详细的教程和代码,但是我没有时间阅读, namin/inc: an incremental approach to compiler construction, 所以只是简单地看了一些这篇论文。我觉得这篇论文以及参考文献可以作为索引,一些基本的编译器实现问题可以在这里找到答案。
这个教学编译器的source language是scheme(应该最终实现了R5RS), machine language是x86 assembly. scheme的好处就是它基本上没有语法以及类型,所以可以将精力放在运行时代码以及代码生成上,而这正是许多教学编译器所缺失的。
编译closure
我们编译器的寄存器约定是:
- %esi 存放生成的closure对象包括:
- 代码地址
- free variabiles的地址或者是值
- %edi 存放当前正在被调用的closure对象.
The funcall evaluated all the arguments as before but skips not one but two stack locations: one to be used to save the current value of the closure pointer, and one for the return point. After the arguments are evaluated and saved, the operator is evaluated, and its value is moved to %edi (whose value must be saved to its stack location). The value of %esp is adjusted and an indirect call through the first cell of the closure pointer is issued. Upon return from the call, the value of %esp is adjusted back and the value of %edi is restored from the location at which it was saved.
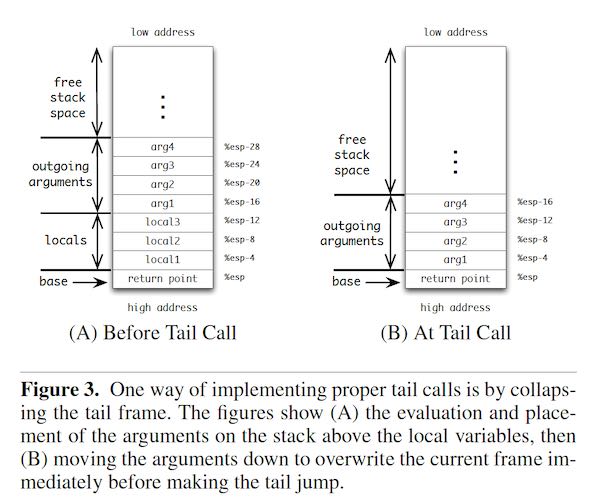
处理尾递归
The Scheme report requires that implementations be properly tail recursive. By treating tail-calls properly, we guarantee that an un bounded number of tail calls can be performed in constant space.
So far, our compiler would compile tail-calls as regular calls followed by a return. A proper tail-call, on the other hand, must perform a jmp to the target of the call, using the same stack position of the caller itself. A very simple way of implementing tail-calls is as follows (illustrated in Figure 3):
- All the arguments are evaluated and saved on the stack in the same way arguments to nontail calls are evaluated.
- The operator is evaluated and placed in the %edi register replacing the current closure pointer.
- The arguments are copied from their current position of the stack to the positions adjacent to the return-point at the base of the stack.
- An indirect jmp, not call , through the address in the closure pointer is issued.
This treatment of tail calls is the simplest way of achieving the objective of the requirement. Other methods for enhancing performance by minimizing the excessive copying are discussed later in Section 4
支持FFI
支持FFI要做三件事情:
- 从动态库中找到符号
- 和C类型之间做转换
- 按照ABI和cdecl方式调用函数
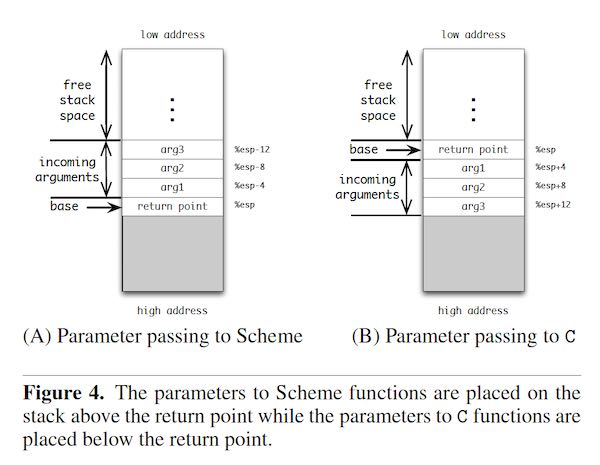
The foreign-call form takes a string literal as the first argument. The string denotes the name of the C procedure that we intend to call. Each of the expressions are evaluated first and their values are passed as arguments to the C procedure. The calling convention for C differs from the calling convention that we have been using for Scheme in that the arguments are placed below the return point and in reverse order. Figure 4 illustrates the difference.
To accommodate the C calling conventions, we evaluate the arguments to a foreign-call in reverse order, saving the values on the stack, adjusting the value of %esp, issuing a call to the named procedure, then adjusting the stack pointer back to its initial position. We need not worry about the C procedure clobbering the values of the allocation and closure pointer because the Application Binary Interface (ABI) guarantees that the callee would preserve the values of the %edi,%esi,%ebp and %esp registers[14].
User-defined macros and a powerful module system can be added simply by compiling and loading the freely-available portable syntax-case implementation [7, 18].
Similarly, we did not handle stack overflows. A stack-based implementation can perform fast stack overflow checks by comparing the stack pointer to an end of stack pointer (held elsewhere) and then jumping to a stack-overflow handler. The handler can allocate a new stack segment and wire up the two stacks by utilizing an underflow handler. Implementing stack overflo and underflow handlers simplifies implementing efficient con tinuationscapture and reinstatement [9]. (捕获overflow/underflow异常, 可以实现自动伸缩堆栈)
Alternatively, we can transform the input program into continuation passing style prior to performing closure conversion. This transformation eliminates most of the stack overflow checks and simplifies the implementation of call/cc. On the down side, more closures would be constructed at run-time causing excessive copying of variables and more frequent garbage col lections. Shao et al. show how to optimize the representation of such closures [15].