alpha-beta剪枝技术
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha%E2%80%93beta_pruning
AB剪枝是基于min-max搜索策略的优化方法,原理就是根据上层已知的值来减少树的搜索。
注意我们这里必须以一致视角来eval game state. 比如下棋,在我方下完之后,就需要评估我方的局面,所以我们希望找到极大值。 在对方下完之后,也必须评估我方的局面,所以对方肯定希望找到我们的极小值。这样有两个好处,一个是max-min搜索和ab剪枝, 另外一方面到了叶子节点上评估函数是一致的. 如果我方是黑棋的话,那么我们始终只需要评估当前棋盘上黑棋的价值。
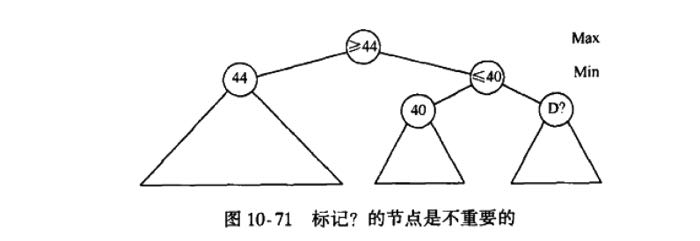
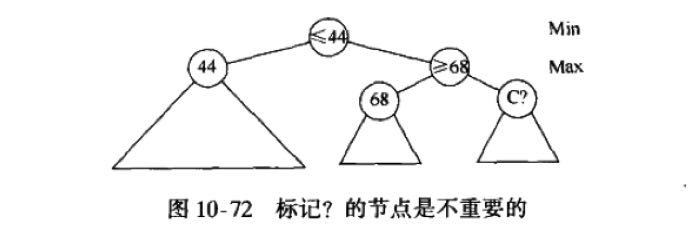
参考下面代码的话,10-71对应的剪枝是alpha cut-off, 10-72对应的是beta cut-off.
function alphabeta(node, depth, α, β, maximizingPlayer) is
if depth = 0 or node is a terminal node then
return the heuristic value of node
if maximizingPlayer then
value := −∞
for each child of node do
value := max(value, alphabeta(child, depth − 1, α, β, FALSE))
α := max(α, value)
if α ≥ β then
break (* β cut-off *)
return value
else
value := +∞
for each child of node do
value := min(value, alphabeta(child, depth − 1, α, β, TRUE))
β := min(β, value)
if α ≥ β then
break (* α cut-off *)
return value
(* Initial call *)
alphabeta(origin, depth, −∞, +∞, TRUE)
我考虑了一下觉得alpha, beta可以缩减成为一个变量,但是不确定是否正确
function alphabeta(node, depth, threshold, maximizingPlayer) is
if depth = 0 or node is a terminal node then
return the heuristic value of node
if maximizingPlayer then
value := −∞
for each child of node do
value := max(value, alphabeta(child, depth − 1, value, FALSE))
if value >= thresold then
break (* β cut-off *)
return value
else
value := +∞
for each child of node do
value := min(value, alphabeta(child, depth − 1, value, TRUE))
if threshold >= value then
break (* α cut-off *)
return value
alphabeta(origin, depth, +∞, True)