Achieving Rapid Response Times in Large Online Services
如何在大规模在线系统中保证延迟?
通常大规模在线系统都是large fanout的,那么非常容易出现延迟。
Server with 1 ms avg. but 1 sec 99%ile latency – touch 1 of these: 1% of requests take ≥1 sec – touch 100 of these: 63% of requests take ≥1 sec
解决办法很直接,就是减少这种variability造成的影响,包括:
- Careful engineering all components of system
- Possible at small scale – dedicated resources – complete control over whole system – careful understanding of all background activities –less likely to have hardware fail in bizarre ways
但是实践系统非常复杂,因为软件和硬件的升级或者是修改都会补偿这种delicate balance.
并且上面这种办法没有办法充分利用资源。大规模系统为了充分利用资源,都会工作在一个共享环境(shared env)下面。整合集群上会有各种各样的任务在运行。
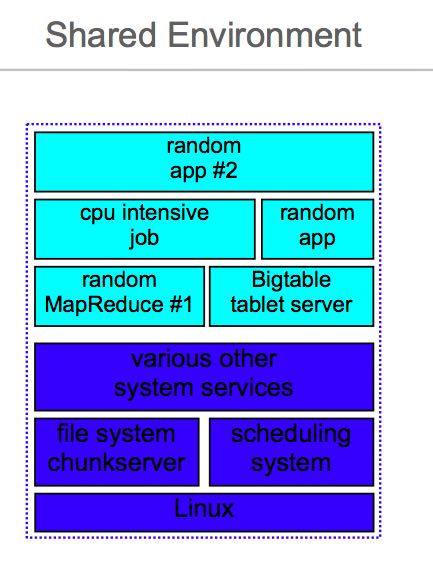

那么如何在共享环境下面还能保证延迟呢?下面三个是基本思路
- Differentiated service classes 为服务划分优先级,比如设置不同优先级的服务队列
- Reduce head-of-line blocking 避免head-of-line的阻塞,把请求切分成为小片
- Manage expensive background activities 管理好开销很大的后台任务,容易影响到在线服务
这些都是从外部来缓解环境对延迟变动造成的影响,接下来是如何从系统内部出发来解决延迟变动。
如果我们将Faults和Variability放在一起看的话,或许会得到一些启发
Tolerating Faults vs. Tolerating Variability
- Tolerating faults.
- make a reliable whole out of unreliable parts, rely on extra resources 从资源角度
- 10s of failures per day, scale of tens of seconds 从时间角度
- Tolerating variability
- make a predictable whole out of unpredictable parts, use these same extra resources
- 1000s of disruptions/sec, scale of milliseconds
所以思路可以是,通过对资源的重复(多个请求)/合理使用(load balance),来减少延迟变动问题。具体地,可以将请求分为下面两类,以及对应的解决办法:
- Cross request adaptation 第一种是多个请求
- examine recent behavior
- take action to improve latency of future requests
- typically relate to balancing load across set of servers
- time scale: 10s of seconds to minutes
- Within request adaptation 第二种是一次请求
- cope with slow subsystems in context of higher level request
- time scale: right now, while user is waiting
第一种请求中,系统要能即使了解自身状况,并且进行合理调节,并且正确引导后面的请求。
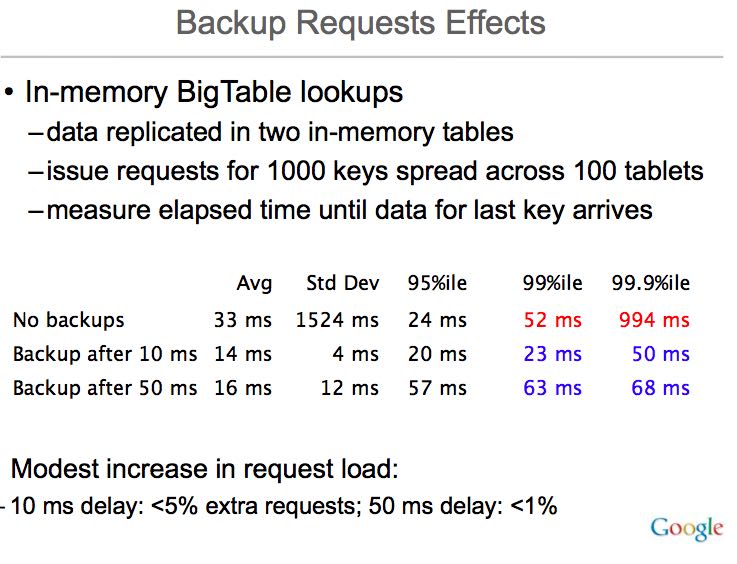
第二种请求中,可以重复请求,两次重复请求时间有一定的时间间隔比如20ms,根据业务而定。ppt里面第一个请求可以称作canary request, 去试探性地看能否及时返回,而后面的请求称作backup requests, 确保延迟变动尽可能低。一旦某个请求成功的话,可以选择性地去取消其他请求。数据上看,效果还是非常显著的。
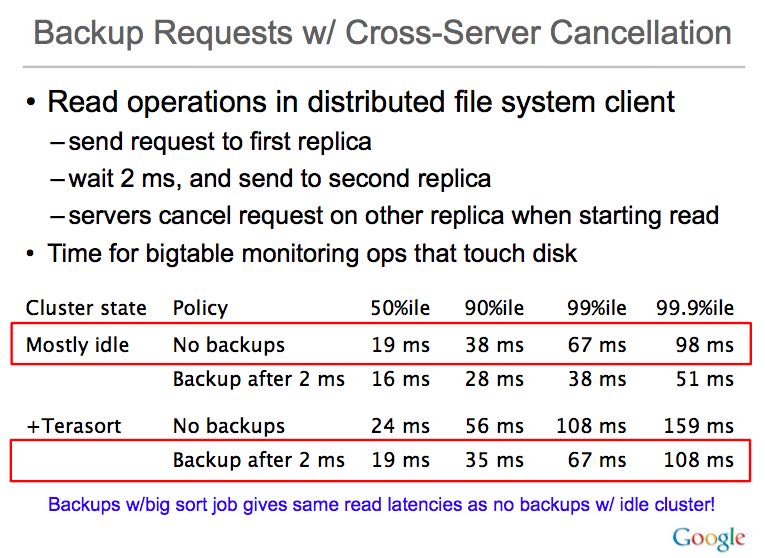
当然这种重复请求也可能造成额外的资源消耗问题,所以为了确认这种办法可以在所有环境下都工作,Jeff给出了两组对比数据,分别是在idle和运行terasort环境下,bigtable记录的访问磁盘的操作延迟。同样效果显著。
另外一个减少Variability思路是,只返回部分结果。一旦发现某个subsystem返回时间太长的话,舍弃这个部分的结果(或许之后会切断这个subsystem的访问)。但是不要忘记在cache里面标注这个结果不是完整的。
一些硬件发展趋势对延迟变动性的影响
- Some good: lower latency networks make things like backup request cancellations work better
- Some not so good: – plethora of CPU and device sleep modes save power, but add latency variability – higher number of “wimpy” cores => higher fanout => more variability
- Software techniques can reduce variability despite increasing variability in underlying hardware